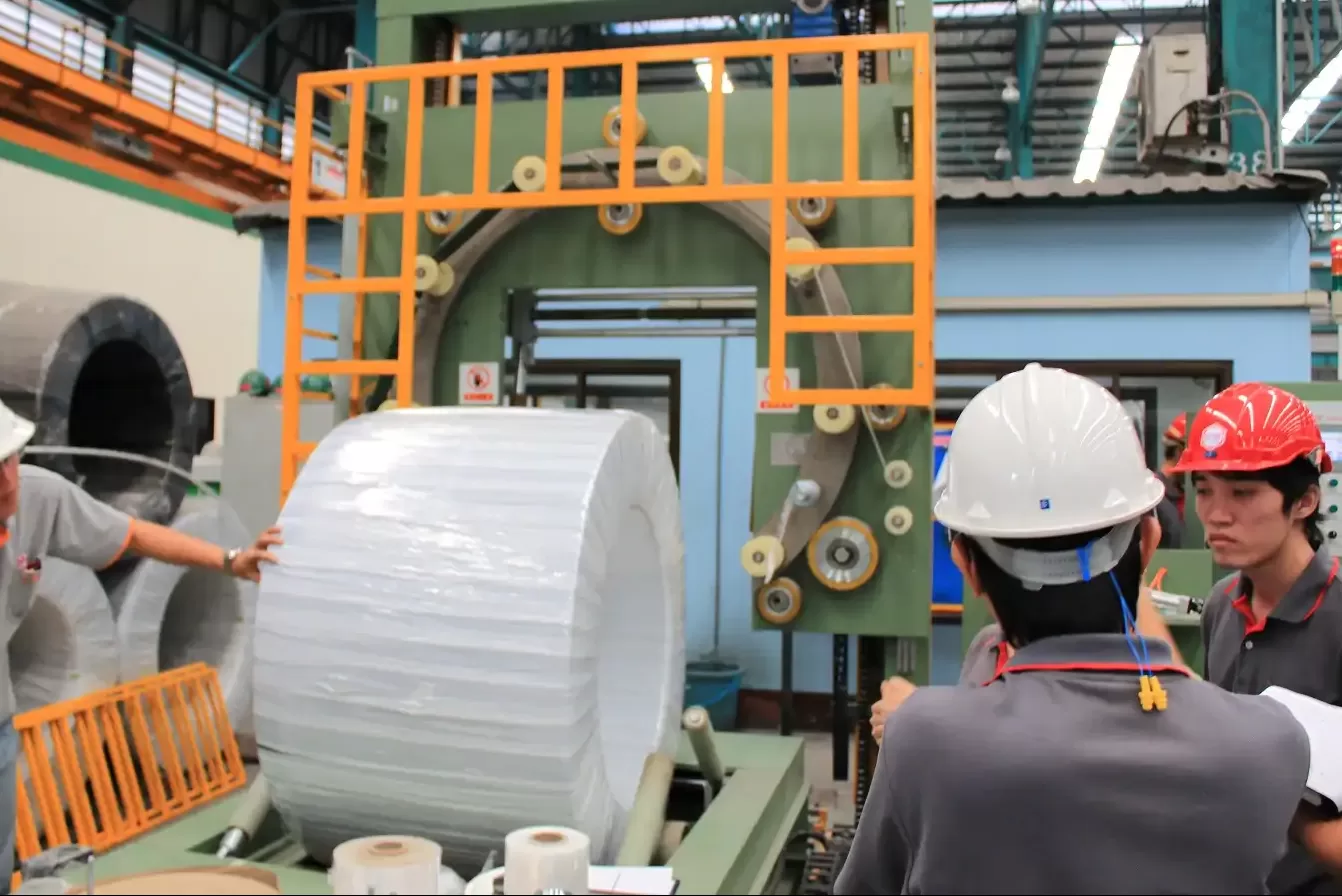
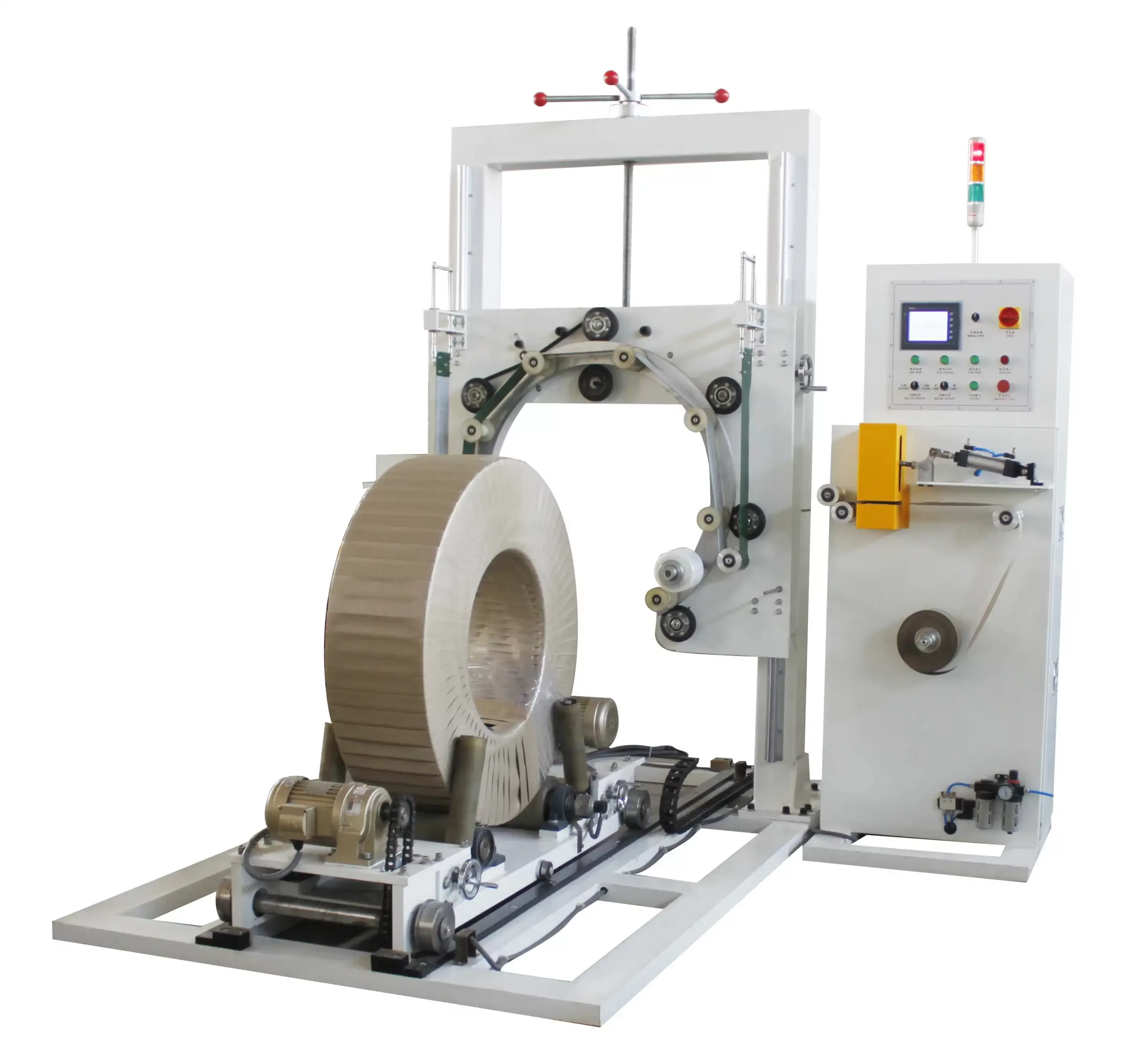
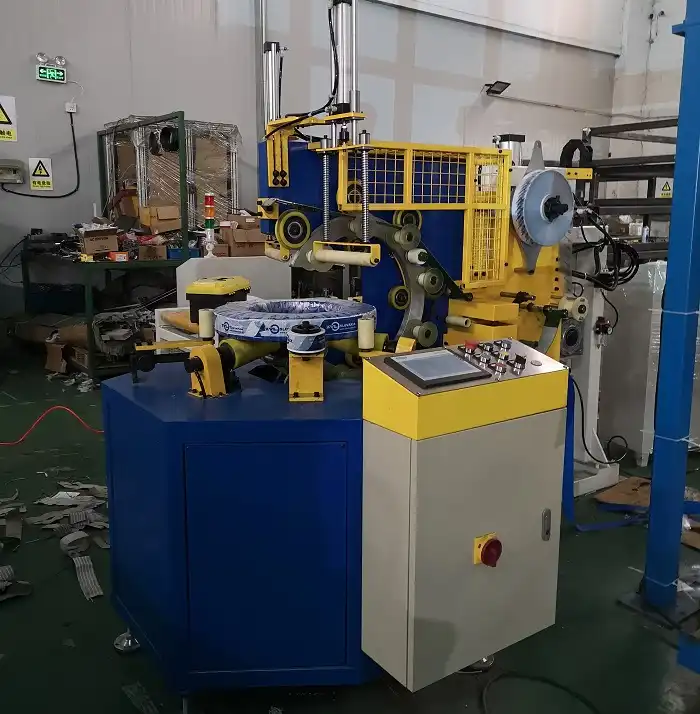
In today’s globalized marketplace, ensuring the safe and efficient packaging of steel wire is paramount. For businesses involved in manufacturing or distributing steel wire products, understanding and adhering to the necessary safety certifications is not just a matter of regulatory compliance—it’s a commitment to quality, safety, and operational excellence.

Safety certifications for steel wire packing typically include ISO standards for general machinery safety, CE marking for European markets, and potentially UL or CSA certifications for North America. Specific certifications depend on the equipment used (like wrapping machines) and the destination market, ensuring worker safety, preventing product damage, and meeting legal requirements.

Navigating the landscape of safety certifications can seem complex, but it is essential for protecting your operations and your reputation. This article will delve into the key safety certifications required for steel wire packing, helping you understand the standards, why they matter, and how to ensure your operations are fully compliant and safe.
1. Decoding Industry Standards for Steel Wire Packing Safety
Industry standards are the backbone of safe and efficient operations across all sectors, and steel wire packing is no exception. These standards are developed by expert bodies to ensure consistency, quality, and above all, safety in manufacturing processes and equipment.
Industry standards for steel wire packing equipment are crucial for ensuring operator safety, machine reliability, and product integrity. These standards, such as ISO 12100 for machine safety and relevant regional standards like ANSI B11 in North America or the European Machinery Directive, provide frameworks for risk assessment, safeguarding, and safe machine design.
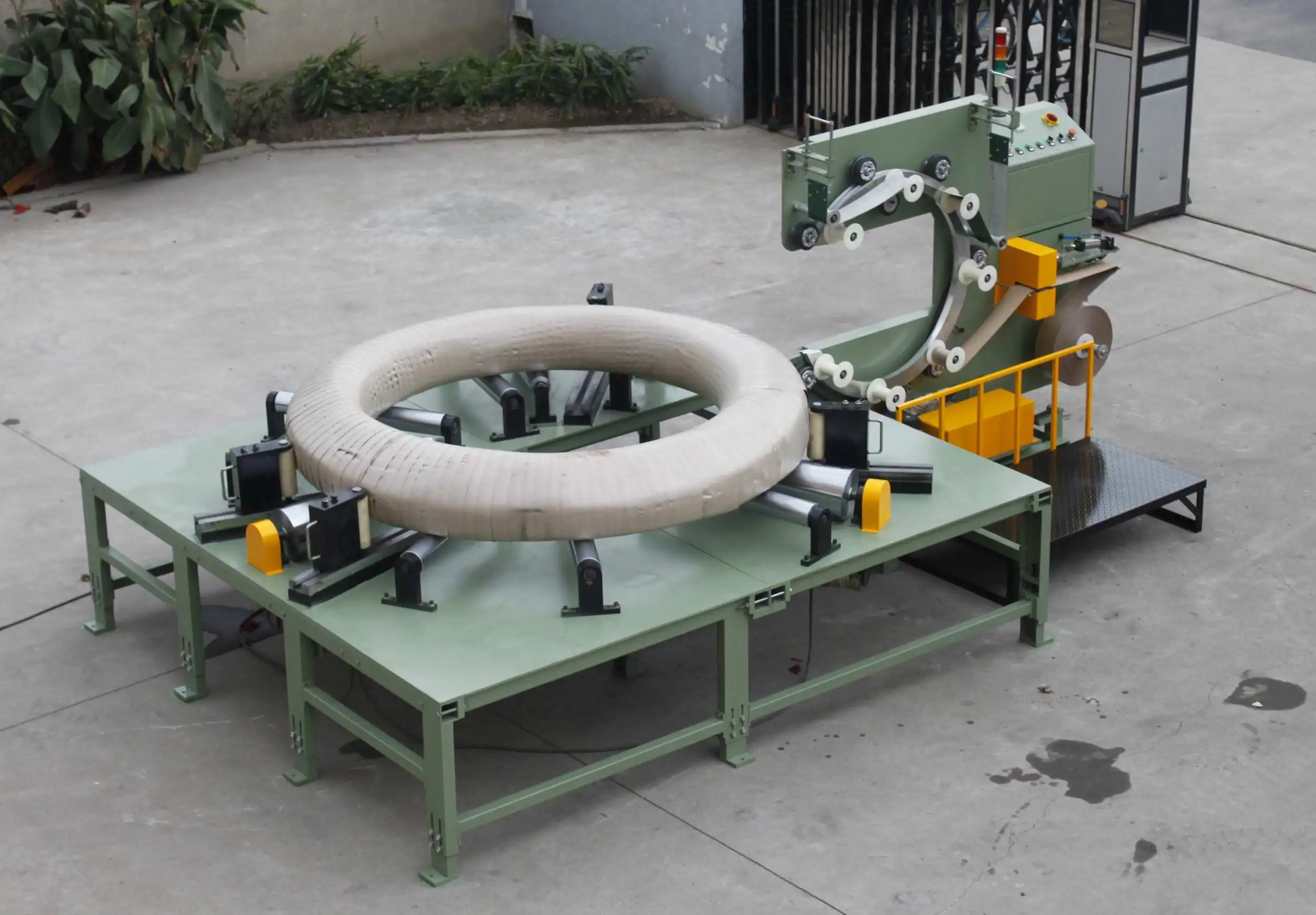

To truly grasp the importance of these standards, we need to break down what they entail and why adherence is not just beneficial, but critical. Let’s examine the layers of industry standards that impact steel wire packing operations.
The Multi-Layered Approach to Industry Standards in Steel Wire Packing
Industry standards for steel wire packing are not monolithic; they are a collection of different types of guidelines and regulations that address various aspects of safety and operation. Understanding these layers is key to comprehensive compliance.
1.1.1. General Machinery Safety Standards: The Foundation
At the base level, we have general machinery safety standards that apply broadly across industries. ISO 12100, "Safety of machinery — General principles for design — Risk assessment and risk reduction," is perhaps the most globally recognized standard in this category. It provides a framework for risk assessment and reduction during the design and manufacture of machinery. For steel wire packing, this means that machinery manufacturers must follow a systematic process to identify hazards, assess risks, and implement protective measures.
1.1.2. Regional and National Standards: Tailoring to Local Requirements
Beyond the general standards, regional and national bodies introduce specific requirements that reflect local laws and safety cultures.
| Region/Nation | Key Standards Body | Relevant Standards for Machinery | Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Europe | European Union | Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, EN standards (harmonized) | CE Marking, Essential Health and Safety Requirements |
| North America | ANSI, CSA, UL | ANSI B11 series, CSA standards, UL standards | OSHA compliance, NRTL certification, Electrical safety |
| Canada | CSA | CSA standards | Canadian specific safety requirements |
| USA | ANSI, UL | ANSI B11 series, UL standards | OSHA compliance, Electrical safety, UL Listing |
| International | ISO | ISO standards (e.g., ISO 12100) | Global best practices, harmonization |
For instance, in Europe, the Machinery Directive mandates CE marking for machinery, indicating conformity with essential health and safety requirements. This often involves adhering to harmonized European Norms (EN standards) that detail specific safety aspects for various types of machinery. In North America, ANSI B11 standards provide detailed guidelines for machine tools, while organizations like UL and CSA offer certifications that are widely recognized and often required for insurance and regulatory purposes. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) regulations in the U.S. also play a crucial role, setting legal requirements for workplace safety, including machine guarding and safe operating procedures.
1.1.3. Industry-Specific Standards: Refining for Wire Packing
While general and regional standards provide a broad framework, industry-specific standards hone in on the unique risks and requirements of steel wire packing. Currently, there may not be highly specific "steel wire packing standards" as a standalone category, but relevant standards from related industries, such as metalworking or packaging, are applied. For example, standards related to coil handling, tension control, and cut-off mechanisms in metal processing machinery can be relevant. Similarly, packaging industry standards focusing on automation safety, emergency stops, and safeguarding are applicable to wire packing machines.
1.1.4. The Importance of a Holistic Approach
Navigating these layers requires a holistic approach. Manufacturers and users of steel wire packing machinery need to consider:
- Destination Market: Where will the machinery be used? This dictates regional and national mandatory certifications (e.g., CE marking for Europe, potentially UL/CSA for North America).
- Machine Type: What specific operations does the machinery perform? This determines which specific machinery safety standards are most relevant (e.g., for wrapping, strapping, or cutting).
- Risk Assessment: A thorough risk assessment, as per ISO 12100, is fundamental to identify hazards and determine necessary safety measures, regardless of specific standards.
- Best Practices: Even beyond mandatory requirements, adopting best practices from recognized standards bodies enhances safety and operational efficiency.
By understanding and applying this multi-layered approach to industry standards, businesses in steel wire packing can ensure they are not just compliant, but also operating at the highest levels of safety and efficiency. This proactive stance minimizes risks, protects workers, and builds a reputation for quality and responsibility.
2. Essential Safety Certifications for Wire Packing Machines
When it comes to wire packing machines, certain safety certifications are essential to ensure the equipment meets recognized safety benchmarks and regulatory demands. These certifications vary by region but commonly include marks that indicate compliance with electrical safety, machine safety, and sometimes, specific performance criteria.
Key safety certifications for wire packing machines include CE Marking for Europe, indicating compliance with the Machinery Directive; UL and CSA certifications for North America, focusing on electrical and safety standards; and ISO certifications like ISO 12100, demonstrating adherence to international safety design principles. These certifications assure users of the machine’s safety and compliance.
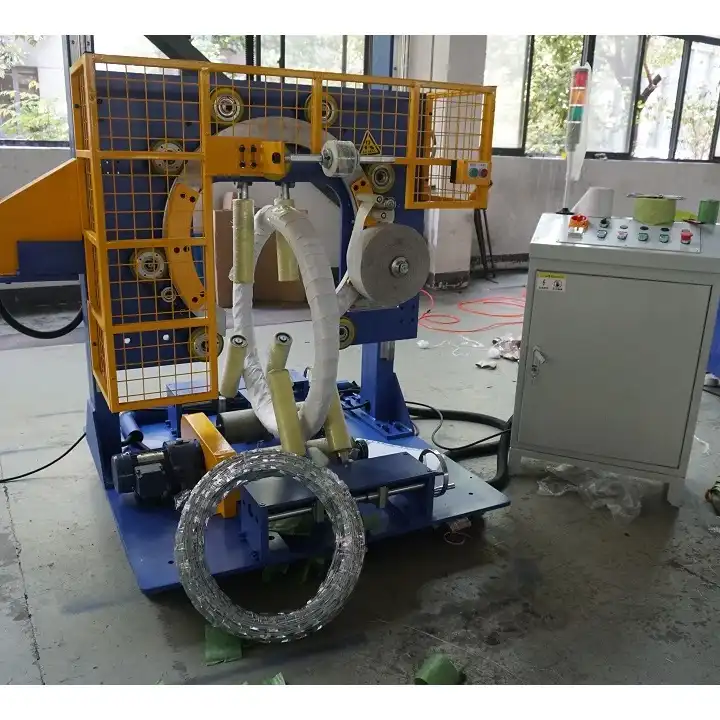

Let’s delve into the most critical certifications that manufacturers and users should be aware of when dealing with wire packing machinery.
Decoding Key Safety Certifications: A Closer Look
Understanding what each certification represents and its geographical relevance is vital for making informed decisions about machinery procurement and deployment.
2.1. CE Marking: Your Passport to the European Market
The CE mark is not just a certification; it’s a declaration by the manufacturer that the product meets all the applicable provisions of certain relevant European health, safety, and environmental protection legislation. For wire packing machinery intended for the European Economic Area (EEA), CE marking is mandatory. It signifies compliance with directives like the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, which covers a broad spectrum of safety requirements for machinery.
Achieving CE marking involves:
- Risk Assessment: Conducting a thorough risk assessment to identify hazards associated with the machine.
- Compliance with Directives: Ensuring the machine design and manufacturing comply with the Essential Health and Safety Requirements (EHSRs) of the Machinery Directive.
- Technical Documentation: Preparing comprehensive technical documentation that details the design, manufacturing, and operation of the machine, along with risk assessment results and applied standards.
- Declaration of Conformity: Signing a Declaration of Conformity, formally stating that the machine meets the requirements of the applicable directives.
- Affixing the CE Mark: Once all requirements are met, the manufacturer can affix the CE mark to the machine.
2.2. UL and CSA Certifications: North American Benchmarks
In North America, particularly in the United States and Canada, UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and CSA (Canadian Standards Association) certifications are highly recognized and often essential. While not strictly mandatory by federal law in all cases, these certifications are widely accepted by regulatory bodies (like OSHA), insurance companies, and customers as proof of product safety.
- UL Certification: UL is a globally recognized safety science organization. UL certifications for machinery, including wire packing machines, primarily focus on electrical safety but also consider other safety aspects. A "UL Listed" mark indicates that representative samples of the product have been tested and found to meet UL’s published safety standards.
- CSA Certification: CSA Group is another leading standards development and testing organization. CSA certifications are similar to UL in scope and recognition within North America. CSA marks indicate that a product has been tested to applicable CSA standards, which often align closely with or are equivalent to UL and ANSI standards.
For wire packing machinery, UL and CSA certifications typically cover:
- Electrical Safety: Ensuring the machine’s electrical components and wiring meet safety standards to prevent electrical shock and fire hazards.
- Mechanical Safety: Verifying that mechanical safeguards, such as guards and interlocks, are in place and effective in protecting operators from moving parts.
- Fire Safety: Assessing materials and design to minimize fire risks.
2.3. ISO 9001 and ISO 12100: Quality and Safety Management Foundations
Beyond product-specific certifications, ISO standards play a vital role in establishing a framework for quality and safety management within manufacturing organizations.
- ISO 9001: Quality Management System: ISO 9001 is a globally recognized standard for quality management systems. While not directly a safety certification for machinery, ISO 9001 certification demonstrates a company’s commitment to quality processes, which indirectly supports safety by ensuring consistent manufacturing and quality control.
- ISO 12100: Safety of Machinery – General Principles for Design: As mentioned earlier, ISO 12100 is a fundamental standard for machinery safety design. While there isn’t a specific "ISO 12100 certification" mark to affix to a machine, demonstrating adherence to ISO 12100 principles is crucial for CE marking and for general best practices in machinery safety design worldwide.
2.4. Other Relevant Certifications and Marks
Depending on the specific type of wire packing machine and its intended use, other certifications or marks might be relevant:
- NRTL Listing (North America): For OSHA compliance in the U.S., certification by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL), such as UL or ETL, is often required. CSA is also recognized as an NRTL in the U.S.
- EAC Mark (Eurasian Economic Union): For markets within the Eurasian Economic Union (Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Armenia, Kyrgyzstan), the EAC mark is required, indicating compliance with technical regulations of the customs union.
Choosing machinery with the appropriate safety certifications is a critical step in ensuring operational safety and regulatory compliance. Understanding these certifications empowers businesses to make informed procurement decisions and prioritize safety in their steel wire packing processes.
3. The Tangible Benefits of Using Certified Wire Packing Machinery
Investing in certified wire packing machinery is more than just ticking a compliance box—it brings a wealth of tangible benefits that impact operational efficiency, safety, and overall business success. These benefits extend from reduced risks and liabilities to enhanced productivity and customer trust.
Utilizing certified wire packing machinery offers numerous benefits, including enhanced safety for operators, reduced risk of accidents and liabilities, ensured regulatory compliance, improved machine reliability and uptime, and increased customer confidence in product quality and safety. These advantages contribute to a more efficient, safe, and reputable operation.
Let’s explore the concrete advantages that certified machinery brings to steel wire packing operations, showcasing why it’s a sound investment rather than just an expense.
Unpacking the Benefits: Why Certification Matters
The advantages of certified wire packing machinery are multifaceted, touching on critical areas of business performance and sustainability.
3.1. Enhanced Operator Safety and Reduced Workplace Accidents
Perhaps the most paramount benefit is the enhanced safety for machine operators and other personnel in the workplace. Certified machinery is designed and manufactured to minimize hazards, incorporating safety features like:
- Effective Guarding: Physical barriers that prevent access to dangerous moving parts.
- Safety Interlocks: Systems that stop the machine if guards are opened or safety devices are triggered.
- Emergency Stop Mechanisms: Readily accessible buttons to quickly halt machine operation in emergencies.
- Ergonomic Design: Features that reduce operator fatigue and strain, minimizing human error.
- Clear Safety Signage and Warnings: Visible instructions and alerts about potential hazards and safe operating procedures.
By reducing the risk of accidents and injuries, certified machinery contributes to a safer work environment, boosting employee morale, reducing absenteeism, and lowering costs associated with workplace injuries and compensation claims.
3.2. Ensured Regulatory Compliance and Minimized Legal Liabilities
Compliance with safety regulations is not optional—it’s a legal imperative. Certified machinery helps businesses meet these obligations, avoiding potential fines, penalties, and legal repercussions. Certifications like CE marking, UL, and CSA are often recognized by regulatory bodies as evidence of conformity with relevant safety standards.
Using certified equipment demonstrates due diligence in prioritizing safety, which can be crucial in liability cases. Should an accident occur, demonstrating that certified machinery was in use and properly maintained can mitigate legal risks and demonstrate a commitment to safety.
3.3. Improved Machine Reliability and Uptime
Certified machinery often undergoes rigorous testing and quality control processes during manufacturing to meet certification standards. This scrutiny results in equipment that is generally more reliable and durable. Higher quality components, robust design, and adherence to manufacturing best practices contribute to:
- Reduced Downtime: Fewer unexpected breakdowns and malfunctions, leading to increased production uptime.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: More reliable machinery typically requires less frequent and less extensive maintenance over its lifespan.
- Extended Machine Lifespan: Quality construction and adherence to standards can prolong the operational life of the equipment.
Increased reliability and uptime translate directly to higher productivity and lower operational costs, making certified machinery a financially sound choice in the long run.
3.4. Enhanced Reputation and Customer Confidence
Using certified machinery sends a strong message to customers, partners, and stakeholders about a company’s commitment to quality and safety. It builds trust and enhances reputation in several ways:
- Product Quality Assurance: Certification of machinery indirectly assures customers that the products packaged using this equipment are handled with care and attention to safety and quality.
- Brand Image: Investing in certified equipment aligns with a brand image of responsibility, quality, and ethical operations.
- Competitive Advantage: In markets where safety and quality are paramount, using certified machinery can be a significant differentiator, attracting customers who value these aspects.
In conclusion, the benefits of using certified wire packing machinery are far-reaching and impactful. They encompass safety, compliance, operational efficiency, and business reputation, making certification a strategic advantage for any organization involved in steel wire packing.
4. Maintaining Compliance and Ensuring Ongoing Safety
Acquiring certified wire packing machinery is a significant step, but maintaining ongoing compliance and ensuring continuous safety is an equally important, ongoing process. Certifications are not a one-time achievement; they require sustained effort and vigilance throughout the machine’s operational life.

Maintaining compliance for certified wire packing machinery involves regular inspections, adherence to maintenance schedules recommended by manufacturers and certification bodies, proper operator training, and diligent record-keeping. Regular audits and updates to safety protocols are also crucial to ensure continued safe and compliant operation.
Sustaining safety and compliance requires a proactive and systematic approach. Let’s outline the key practices for ensuring your certified wire packing machinery remains safe and compliant over time.
Best Practices for Sustaining Safety and Compliance:
-
Regular Inspections and Maintenance:
- Scheduled Inspections: Implement a schedule for routine inspections of safety features, guards, interlocks, emergency stops, and electrical systems. Follow manufacturer guidelines and relevant standards for inspection frequency and scope.
- Preventive Maintenance: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule. Regular lubrication, parts replacement, and system checks are crucial for maintaining machine reliability and safety.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of all inspections, maintenance activities, and repairs. This documentation is essential for demonstrating ongoing compliance and can be valuable for troubleshooting and future maintenance planning.
-
Operator Training and Competency:
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Provide thorough training to all machine operators, covering safe operating procedures, emergency shutdown protocols, hazard awareness, and basic maintenance tasks.
- Regular Refresher Training: Conduct periodic refresher training to reinforce safe practices and update operators on any changes in procedures or safety standards.
- Competency Assessment: Ensure operators are competent to operate the machinery safely. Implement a system for assessing and verifying operator skills and knowledge.
-
Management of Change:
- Formal Change Management Process: Establish a formal process for managing any changes to the machinery, operating procedures, or materials used in packing.
- Risk Assessment for Changes: Before implementing any change, conduct a risk assessment to evaluate its potential impact on safety and compliance.
- Documentation of Changes: Document all changes made to the machinery, including modifications, upgrades, and repairs, and update technical documentation and safety records accordingly.
-
Regular Audits and Compliance Reviews:
- Internal Safety Audits: Conduct periodic internal audits of safety practices, machine condition, and compliance with relevant standards and regulations.
- External Audits (if required): Be prepared for potential audits by certification bodies or regulatory agencies to verify ongoing compliance.
- Compliance Reviews: Stay updated on changes to safety standards and regulations. Regularly review your safety protocols and procedures to ensure they remain current and effective.
-
Emergency Preparedness:
- Emergency Procedures: Develop and document clear emergency procedures for various scenarios, such as machine malfunctions, accidents, or fires.
- Emergency Drills: Conduct periodic emergency drills to ensure operators and personnel are familiar with emergency procedures and can respond effectively.
- Emergency Equipment: Ensure emergency equipment, such as fire extinguishers and first aid kits, are readily accessible and properly maintained.
By implementing these best practices, businesses can ensure that their investment in certified wire packing machinery continues to deliver on its promise of safety, compliance, and operational excellence throughout its lifecycle. Ongoing vigilance and a commitment to safety culture are key to long-term success.
Conclusion
In the demanding world of steel wire manufacturing and distribution, safety certifications for wire packing are not merely bureaucratic hurdles—they are cornerstones of responsible and efficient operations. From ensuring operator safety and minimizing workplace accidents to guaranteeing regulatory compliance and enhancing product quality, the benefits of adhering to safety standards and utilizing certified machinery are undeniable.
By understanding the landscape of industry standards, recognizing essential certifications like CE marking, UL, and CSA, and committing to ongoing maintenance and compliance, businesses can create a safer, more productive, and more reputable wire packing environment. Investing in certified wire packing machinery is an investment in your workforce, your operations, and your long-term success in the global marketplace. It’s a clear demonstration that safety and quality are not just priorities, but integral values driving your business forward.








