What Methods Can Reduce Noise from Mold Flippers?
Mold flippers are essential machinery in manufacturing, known for efficiently handling heavy molds. However, the operation of these powerful machines can generate significant noise, posing challenges to workplace safety and comfort. Understanding and implementing effective noise reduction methods is crucial for creating a healthier and more productive industrial environment.
Several methods can effectively reduce noise from mold flippers, including implementing sound dampening materials, optimizing hydraulic systems for quieter operation, and regular machinery maintenance. Enclosing noisy components and using vibration isolation techniques also significantly contribute to noise reduction, creating a safer and more comfortable workspace. By addressing noise at its source and along its transmission path, industries can mitigate the harmful effects of excessive sound levels.
This article delves into practical strategies for minimizing noise generated by mold flippers, exploring various techniques and technologies that contribute to a quieter and more efficient operational environment.
1. Implementing Sound Dampening Materials in Mold Flipper Construction
The construction of a mold flipper plays a pivotal role in its noise emission. Integrating sound dampening materials directly into the machine’s design is a proactive approach to minimizing noise generation at the source. These materials can absorb and dissipate sound energy, preventing it from radiating outwards and contributing to overall workplace noise levels.
Sound dampening materials, such as acoustic foam and damping composites, are strategically incorporated into mold flipper construction to absorb vibrations and reduce noise. Applying these materials to machine panels, housings, and platforms minimizes sound resonance and transmission. This approach significantly decreases operational noise, creating a quieter and safer working environment. Effective material selection and placement are key to maximizing noise reduction benefits.
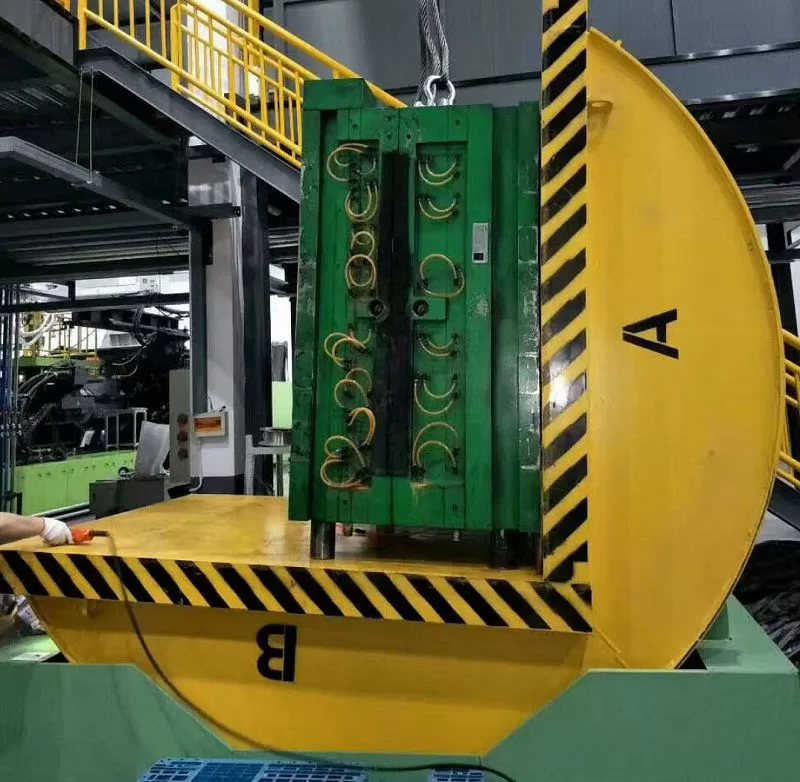

Enhancing Noise Reduction with Advanced Material Application Techniques
Beyond simply incorporating sound dampening materials, the how and where of their application are critical for optimal noise reduction. Advanced techniques ensure that these materials are used most effectively, targeting key noise generation points and maximizing their sound absorption capabilities. This involves a detailed understanding of the mold flipper’s operational mechanics and noise propagation pathways.
Strategic Layering for Enhanced Absorption
One advanced technique is strategic layering. This involves combining different types of sound dampening materials with varying acoustic properties to address a broader spectrum of noise frequencies. For instance, a layer of dense, heavy material can be used to block lower frequencies, while a layer of porous acoustic foam effectively absorbs higher frequencies. This multi-layered approach provides comprehensive noise control across the sound spectrum.
Constrained Layer Damping for Vibration Reduction
Constrained layer damping (CLD) is another highly effective technique. CLD involves applying a damping material between two layers of stiffer material, such as metal. When vibrations occur, the damping material shears, converting vibrational energy into heat and significantly reducing noise radiated from vibrating surfaces. This is particularly useful for large panels and structural components of the mold flipper that tend to resonate and amplify noise.
Material Selection Based on Frequency Analysis
A critical aspect of advanced material application is frequency analysis. Before selecting and applying materials, a noise frequency analysis of the mold flipper in operation should be conducted. This analysis identifies the dominant noise frequencies produced by the machine. Based on this data, materials specifically designed to absorb those frequencies can be chosen, leading to targeted and efficient noise reduction. Different materials excel at absorbing different frequency ranges, as shown in the table below:
| Material Type | Primary Frequency Range | Absorption Coefficient (Example) | Application Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acoustic Foam (Porous) | High Frequencies | 0.7 – 0.9 | Enclosures, panels, housings |
| Damping Composites | Mid to High Frequencies | 0.5 – 0.8 | Machine guards, structural components |
| Heavy Layer Barriers | Low Frequencies | 0.8 – 0.95 | Base structures, machine foundations, enclosures |
| Constrained Layer Damping | Broad Spectrum | Varies based on configuration | Large panels, vibrating surfaces |
By employing these advanced material application techniques, manufacturers can significantly enhance the noise reduction capabilities of mold flippers, creating quieter and more comfortable industrial environments. This targeted and scientific approach to sound dampening material usage moves beyond simple application and into the realm of precision noise engineering.
2. Optimizing Hydraulic Systems for Quieter Mold Flipper Operation
Hydraulic systems are the powerhouse behind mold flippers, providing the force and control needed for heavy mold handling. However, traditional hydraulic systems can be a significant source of noise. Optimizing these systems for quieter operation is a crucial step in reducing overall mold flipper noise.
Quieter hydraulic systems in mold flippers are achieved through strategies like using low-noise pumps, optimizing hose routing to minimize pressure fluctuations, and incorporating accumulators to reduce pressure peaks. These enhancements minimize hydraulic noise generation at its source, leading to a significant reduction in overall machine noise. Careful design and component selection in the hydraulic system are key to achieving quieter operation.
Deep Dive into Hydraulic System Noise Reduction Strategies
Reducing noise in hydraulic systems requires a multifaceted approach, targeting various noise generation mechanisms within the system. From pump design to fluid management, several engineering strategies can be employed to create a significantly quieter hydraulic operation in mold flippers.
Low-Noise Hydraulic Pump Technologies
The hydraulic pump is often the primary noise source in a hydraulic system. Switching to low-noise pump technologies is a fundamental step in noise reduction. Several types of pumps are designed for quieter operation:
- Screw Pumps: These pumps offer smooth, continuous flow with minimal pressure pulsation, resulting in significantly lower noise levels compared to traditional gear or vane pumps.
- Internal Gear Pumps: Designed with gears that mesh internally, these pumps offer quieter operation and reduced flow ripple compared to external gear pumps.
- Variable Displacement Pumps: By adjusting flow rate to match demand, these pumps reduce unnecessary fluid flow and pressure build-up, minimizing noise and energy consumption.
Choosing the right low-noise pump technology, tailored to the specific pressure and flow requirements of the mold flipper, is crucial for effective noise mitigation.
Optimized Hose and Piping Design
Hydraulic hose and piping design significantly impacts noise levels. Turbulent flow, pressure pulsations, and vibrations in hydraulic lines can generate substantial noise. Optimizing hose routing and piping layout can minimize these noise sources:
- Smooth Bends and Gradual Transitions: Avoiding sharp bends and using gradual transitions in piping reduces turbulence and pressure drops, leading to quieter flow.
- Proper Hose Clamping and Isolation: Securely clamping hoses and isolating them from machine structures prevents vibration transmission and reduces noise radiation.
- Pressure Accumulators: Incorporating accumulators in the hydraulic circuit helps dampen pressure pulsations and smooth out pressure peaks, reducing noise and improving system stability.
Fluid Management and Maintenance
Hydraulic fluid condition and maintenance play a vital role in noise reduction. Contaminated or degraded fluid can lead to increased pump wear, cavitation, and noise.
- Regular Fluid Filtration and Replacement: Maintaining clean hydraulic fluid through regular filtration and timely replacement minimizes wear and noise.
- Temperature Control: Excessive hydraulic fluid temperature can increase viscosity and lead to cavitation noise. Implementing cooling systems or optimizing system design to manage heat build-up is important.
- System Bleeding: Entrapped air in the hydraulic system can cause cavitation and noise. Regular system bleeding to remove air is essential.
By implementing these hydraulic system optimization strategies, mold flipper manufacturers can drastically reduce operational noise, creating a more pleasant and productive work environment. This focus on hydraulic noise reduction is a key component of designing truly quiet and efficient mold handling machinery.
3. Regular Maintenance and Component Checks for Noise Reduction
While design and material choices are critical, ongoing maintenance is equally vital for sustained noise reduction in mold flippers. Regular checks and proactive maintenance can prevent noise escalation due to wear and tear, ensuring long-term quiet operation.
Consistent maintenance of mold flippers is essential for keeping noise levels low. Regularly inspecting and replacing worn components like bearings and gears, lubricating moving parts to reduce friction, and tightening loose fasteners minimizes noise caused by wear and vibration. Proactive maintenance not only reduces noise but also extends the lifespan of the machinery. A well-maintained machine operates more quietly and efficiently.
Implementing a Proactive Maintenance Schedule for Noise Control
A reactive approach to maintenance—addressing issues only when they become apparent—is insufficient for effective long-term noise control. A proactive, scheduled maintenance program is crucial for identifying and mitigating potential noise sources before they escalate. This involves regular inspections, lubrication, and timely component replacements.
Key Maintenance Checks and Frequencies
A comprehensive maintenance schedule should include the following checks, performed at the recommended frequencies:
| Component | Check/Maintenance Activity | Frequency | Noise Reduction Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bearings | Inspect for wear, lubrication, and replace if necessary | Monthly/Quarterly | Reduces friction and grinding noise |
| Gears | Inspect for wear, proper meshing, lubrication | Monthly/Quarterly | Prevents gear grinding and excessive backlash noise |
| Fasteners | Check and tighten all bolts and screws | Weekly/Monthly | Eliminates rattling and vibration-induced noise |
| Hydraulic Hoses | Inspect for leaks, wear, and secure clamping | Monthly/Quarterly | Prevents hydraulic noise from leaks and vibrations |
| Lubrication Points | Lubricate all moving parts as per manufacturer guidelines | Weekly/Monthly | Reduces friction and squeaking noise |
| Vibration Isolators | Inspect for wear and effectiveness, replace if needed | Annually/Bi-annually | Maintains isolation efficiency, preventing noise transfer |
Utilizing Condition Monitoring Technologies
Modern condition monitoring technologies can significantly enhance proactive maintenance for noise control. These technologies provide real-time data on machine health, allowing for early detection of potential noise-generating issues:
- Vibration Analysis: Sensors monitor vibration levels, identifying imbalances, bearing wear, and other issues before they become significant noise sources.
- Acoustic Monitoring: Specialized microphones and software analyze machine sounds, detecting abnormal noises that indicate developing problems.
- Thermography: Infrared cameras detect heat build-up in components, which can be an early sign of friction, wear, and potential noise issues.
By integrating condition monitoring into the maintenance program, industries can move towards predictive maintenance, addressing potential noise problems before they arise and ensuring consistently quiet mold flipper operation. This data-driven approach maximizes both noise reduction and machine longevity.
4. Enclosure and Vibration Isolation Techniques
Beyond machine-level modifications, environmental control measures like enclosures and vibration isolation can significantly reduce noise propagation throughout the workplace. These techniques focus on containing noise at its source and preventing its transmission to surrounding areas.
Effective noise reduction often involves a combination of source control and path control. While the previous sections focused on reducing noise at the source (within the mold flipper itself), path control methods, such as enclosures and vibration isolation, prevent noise from traveling and affecting workers.
Enclosing mold flippers with soundproof barriers significantly reduces noise escaping into the workspace. Vibration isolation mounts placed under the machine prevent vibrations, and therefore noise, from transmitting through the floor and structure. Combining enclosures and vibration isolation offers a comprehensive approach to minimizing noise impact. These methods are particularly effective in containing and limiting the spread of machinery noise.
Detailed Explanation of Enclosure and Vibration Isolation:
Enclosures act as barriers that contain the noise generated by the mold flipper. They are constructed from sound-absorbing and sound-blocking materials to minimize noise transmission. Vibration isolation, on the other hand, focuses on decoupling the machine from the building structure to prevent vibrations, which are a significant source of secondary noise, from spreading.
Enclosure Design and Materials:
Effective enclosures are designed to completely or partially surround the mold flipper. Key design considerations include:
- Material Selection: Enclosures are typically constructed using a combination of sound-absorbing materials (like acoustic foam or fiberglass) on the inside to reduce reverberation and sound-blocking materials (like dense panels or laminated gypsum) on the outside to prevent sound transmission.
- Sealing and Gaps: Enclosures must be properly sealed to prevent noise leakage through gaps or openings. Seals around doors and access panels are crucial.
- Ventilation and Access: Enclosures must incorporate ventilation systems to prevent heat build-up inside and provide access for maintenance and operation. Ventilation openings should also be sound-attenuated.
- Window Design: If windows are needed for observation, they should be constructed from laminated or double-glazed soundproof glass.
Vibration Isolation Techniques:
Vibration isolation is achieved by placing vibration isolators between the mold flipper and the floor. These isolators act as springs and dampers, reducing the transmission of vibrations:
- Isolator Types: Common types include rubber mounts, spring isolators, and pneumatic isolators. The choice depends on the machine’s weight, operating frequency, and desired level of isolation.
- Proper Selection and Placement: Isolators must be correctly selected to match the machine’s weight and vibration characteristics. Proper placement is crucial for even weight distribution and effective isolation.
- Foundation Considerations: The foundation beneath the isolators should be stable and level to ensure optimal performance.
By combining well-designed enclosures with effective vibration isolation, industries can create significantly quieter workplaces, protecting employees from noise-induced health risks and improving overall productivity. [(https://www.fhopepack.com/mold-upender.html)Mold flipper noise reduction] is not just about machine modifications, but also about strategically managing the sound environment.
Conclusion
Reducing noise from mold flippers is a multifaceted challenge requiring a combination of engineering solutions and proactive maintenance. Implementing sound dampening materials in the machine’s construction, optimizing hydraulic systems for quieter operation, establishing a rigorous maintenance schedule, and employing enclosure and vibration isolation techniques are all effective strategies. By addressing noise at its source and along its transmission path, industries can create safer, more comfortable, and more productive work environments. Investing in noise reduction is an investment in employee well-being and operational efficiency.
