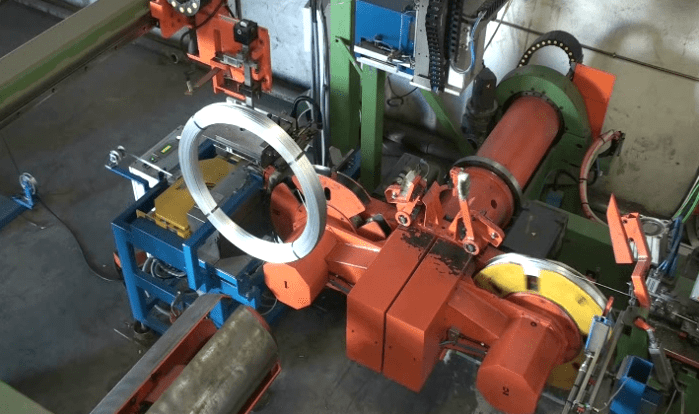
Steel wire, a ubiquitous material in construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure, demands meticulous packaging for safe transportation. Ensuring its integrity from production line to end-user hinges on adhering to stringent packaging requirements that mitigate risks and environmental factors encountered during transit. Proper packaging is not merely an option, but a necessity.
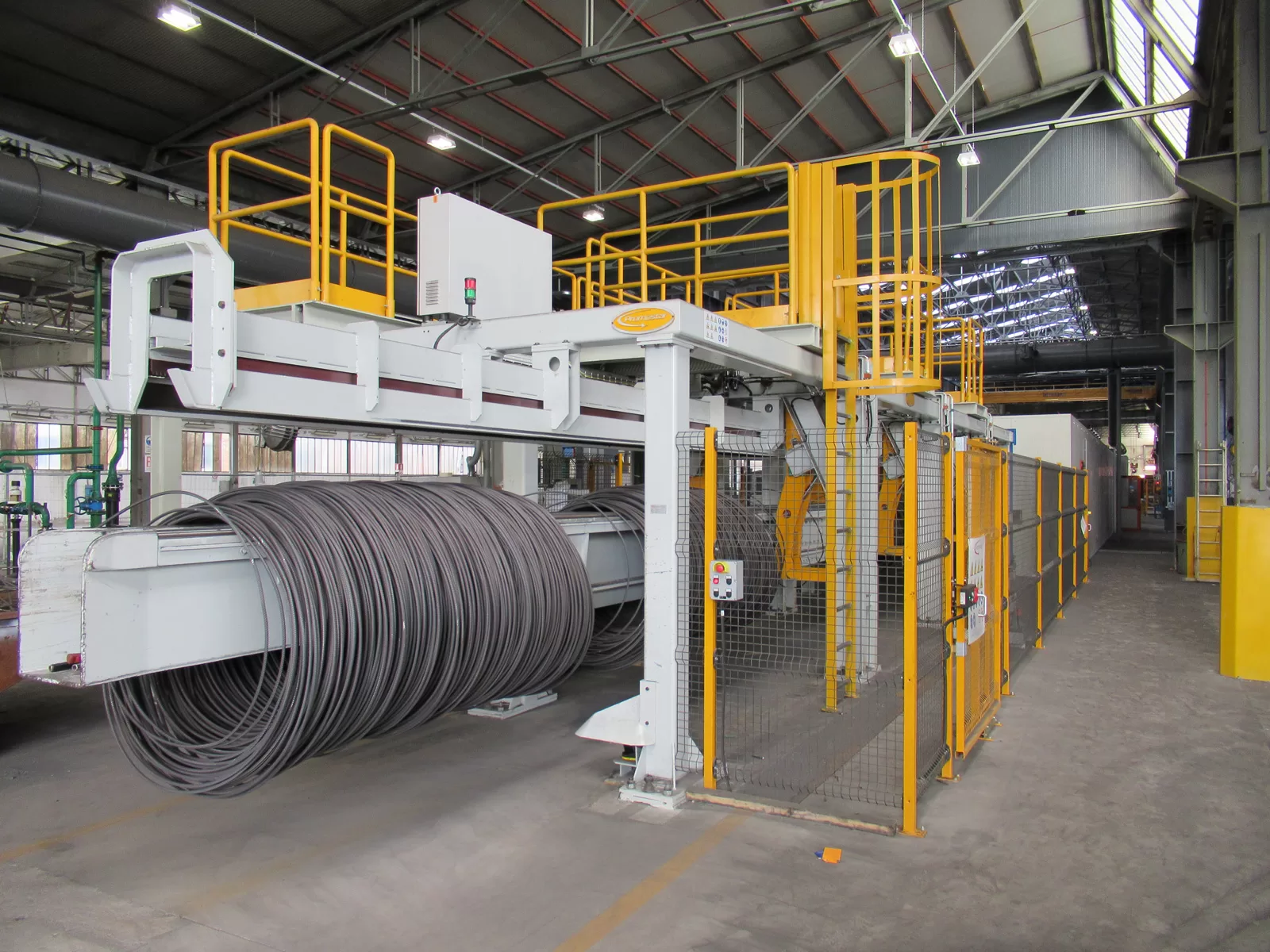

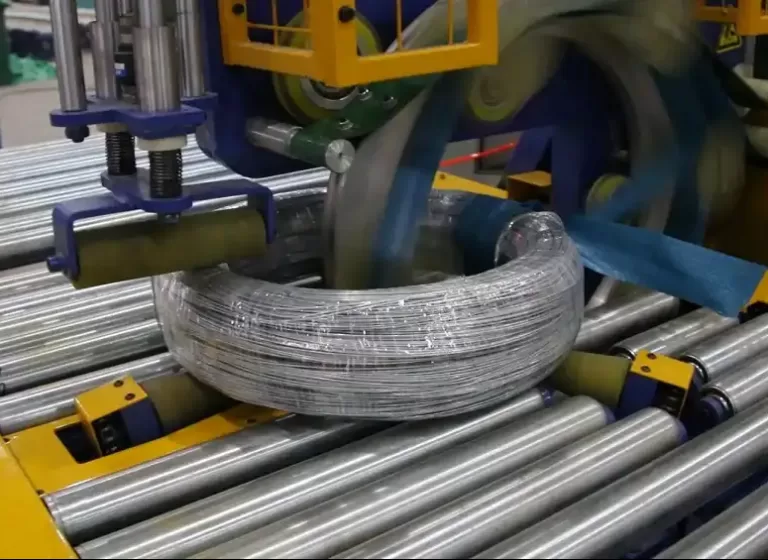
Packaging steel wire for transportation necessitates robust solutions that protect against physical damage, corrosion, and environmental exposure. Key requirements include secure wrapping to prevent unwinding, moisture-resistant materials to combat rust, and sturdy outer packaging capable of withstanding handling and stacking forces. Compliance with shipping regulations is paramount to ensure safe and damage-free delivery.
Navigating the complexities of steel wire packaging requires a comprehensive understanding of industry best practices and regulatory standards. Let’s delve deeper into the critical packaging requirements that safeguard steel wire during its journey.
2. Understanding Regulations and Standards
The transportation of steel wire, like many industrial goods, is governed by a suite of regulations and standards aimed at ensuring safety and preventing damage. These guidelines dictate everything from the materials used in packaging to the methods of securing and labeling shipments. Compliance is not only a legal obligation but also a cornerstone of maintaining product quality and customer satisfaction.
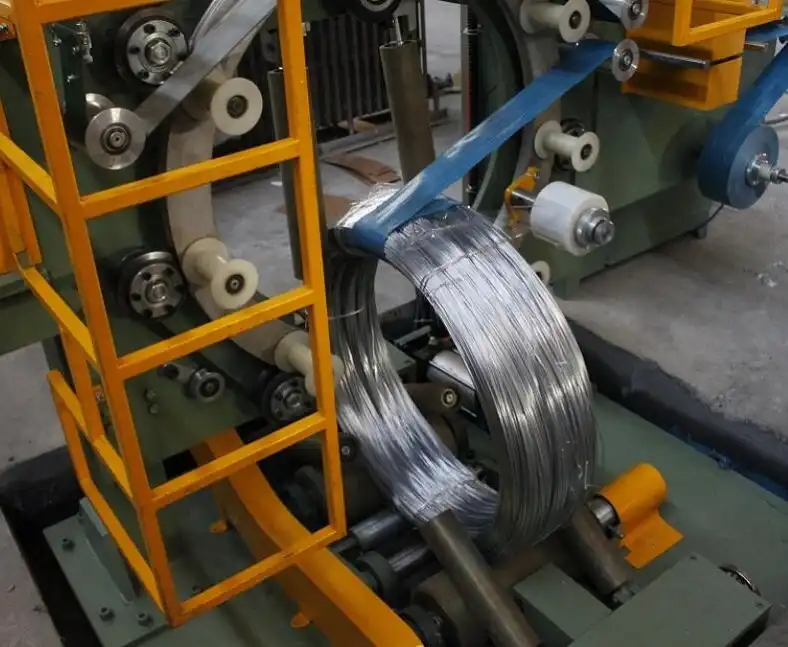

Navigating the landscape of steel wire packaging regulations involves understanding several key directives. Primarily, transportation safety standards, such as those outlined by organizations like the DOT and international maritime guidelines, mandate robust packaging to prevent shifting and damage during transit. These regulations specify performance criteria for packaging materials, requiring them to withstand various stresses like compression, impact, and vibration. Industry standards, such as those from ASTM, further detail best practices for wrapping, banding, and securing steel wire coils to minimize corrosion, unwinding, and physical deformation. Compliance with these layered regulations is crucial for safe and efficient steel wire transportation, ensuring product integrity upon arrival.
To effectively navigate these regulations, it’s essential to break down the key aspects that govern steel wire packaging. Understanding these components will empower businesses to ensure compliance and optimize their packaging strategies.
Decoding Key Regulatory Aspects
Navigating the regulatory landscape for steel wire packaging requires attention to several critical aspects. These can be broadly categorized into material standards, performance testing, documentation, and compliance enforcement. Each aspect plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and integrity of steel wire shipments.
Material Compliance
The selection of packaging materials is not arbitrary; it’s dictated by regulations ensuring adequate protection.
| Material Aspect | Regulatory Focus | Examples | Compliance Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture Barrier | Preventing corrosion; maintaining wire quality | Waterproof wrapping films, rust inhibitors, desiccants | Reduces rust, maintains tensile strength, extends shelf life |
| Strength | Withstanding handling and stacking forces; preventing package failure | High-tensile steel strapping, durable wooden pallets, robust corrugated board | Prevents breakage during handling, ensures safe stacking, minimizes damage from shifting loads |
| Compatibility | Ensuring no reaction between packaging and steel wire | Neutral pH wrapping materials, non-reactive coatings | Prevents chemical reactions that could degrade wire quality or packaging integrity |
Performance Criteria
Packaging must not only be made of compliant materials but also perform under stress.
| Performance Test | Regulatory Purpose | Test Description | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | Simulating handling impacts; ensuring package integrity | Packages are dropped from specified heights onto rigid surfaces in various orientations. | No rupture or loss of contents; minimal damage to packaging that doesn’t compromise safety |
| Compression Test | Simulating stacking loads; preventing package collapse | Packages are subjected to a compressive force for a specified duration, simulating top-load pressure in stacked storage. | Minimal deformation or collapse; packaging must maintain its protective function |
| Vibration Test | Simulating transport vibrations; ensuring securement | Packages are vibrated at varying frequencies and amplitudes to simulate the vibrations experienced during road, rail, or sea transport. | No shifting of contents; packaging remains intact and secure |
Documentation and Certification
Compliance isn’t just about physical packaging; it’s also about paperwork and proof.
| Document Type | Regulatory Requirement | Purpose | Compliance Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shipping Manifest | Required for hazardous materials; details contents, hazards, and emergency procedures | Provides carriers and emergency responders with crucial information about the shipment. | Legal compliance; facilitates safe handling and emergency response |
| Packaging Certification | For specific packaging types; confirms testing and standards adherence | Demonstrates that packaging meets required performance levels and is suitable for the intended hazardous material. | Legal compliance; ensures packaging integrity and safety |
| Compliance Declarations | Shipper’s declaration of conformity to regulations | Asserts that the shipment is prepared and offered for transportation in full compliance with all applicable regulations. | Legal responsibility and accountability; provides assurance to carriers and receivers |
Enforcement and Liability
Failure to comply carries consequences, emphasizing the importance of adherence.
| Aspect | Regulatory Consequence | Impact of Non-Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Inspections | Authorities conduct random and targeted inspections | Potential shipment delays, fines, legal penalties, and reputational damage |
| Fines and Penalties | Significant financial penalties for violations | Direct financial losses; increased operational costs; potential business disruptions |
| Liability | Shippers and carriers are liable for damages | Financial responsibility for damage to goods, injuries, environmental harm; potential legal repercussions and lawsuits |
By understanding these regulatory aspects, stakeholders in the steel wire industry can ensure their packaging practices are not only compliant but also contribute to safer, more efficient, and more reliable transportation.
3. Essential Packaging Materials and Methods
Effective packaging of steel wire goes beyond mere containment; it’s about employing the right materials and methods to create a protective barrier against the rigors of transportation. The selection of these elements directly influences the wire’s condition upon arrival and the overall cost-effectiveness of the shipping process.
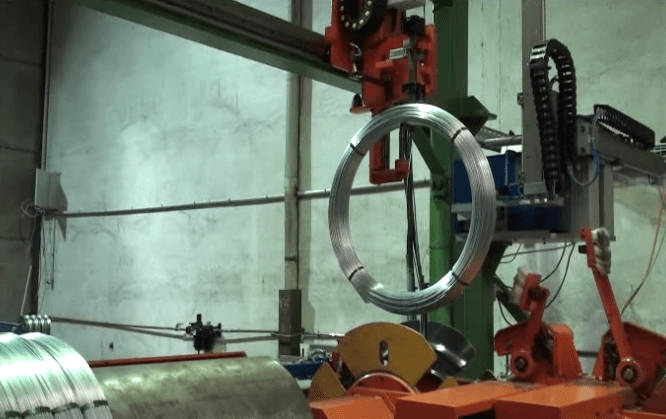
Choosing the correct packaging materials and methods for steel wire transportation is crucial for preventing damage and ensuring cost-efficiency. For coil wrapping, materials like VCI paper, stretch film, and reinforced tapes are essential to prevent corrosion and unwinding. Bundle packaging often utilizes steel strapping, wooden skids, and protective corner boards for stability and resistance to compression and handling forces. For smaller wire products, corrugated boxes with internal cushioning provide adequate protection against impacts and vibrations. The selection depends heavily on the wire type, coil dimensions, weight, and anticipated transportation conditions, balancing protection with economic feasibility.
Exploring the specific materials and methods in detail reveals the nuances of effective steel wire packaging, enabling informed decisions tailored to different transportation needs.
Delving into Packaging Techniques
The art and science of packaging steel wire effectively lie in the nuanced application of various materials and methods. Each technique is tailored to address specific challenges presented by the nature of steel wire and the demands of the [transportation requirements] environment.
Core Wrapping and Protection
The innermost layer of packaging, core wrapping, is crucial for maintaining coil integrity and preventing the initiation of damage.
| Material | Purpose | Application Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| VCI Paper | Corrosion inhibition; moisture barrier | Wrap tightly around the steel wire coil core, ensuring complete coverage. Overlap layers to enhance barrier properties. For long-term storage or humid climates, consider multi-layer wrapping. Secure with tape compatible with VCI properties to maintain airtight seal. |
| Stretch Film | Dust and moisture barrier; coil integrity | Apply in multiple layers with significant overlap to create a robust, water-resistant seal. Tension the film appropriately to ensure a snug fit without excessive pressure that could deform the wire. Consider using specialized stretch films with UV protection for open-deck stowage. |
| Corrugated Cardboard | Physical protection for inner layers; additional cushioning (optional) | Use as an inner layer to add rigidity and protect against punctures. Cut and shape to conform to the coil’s curvature for maximum contact and support. When used with other inner wraps, ensure it doesn’t compromise the primary barrier properties. For heavier coils, consider reinforced or double-wall cardboard for increased strength. Secure with banding or tape to maintain position during handling. |
Coil Wrapping and Securing
The middle layers focus on reinforcing the coil’s structure and providing bulk protection.
| Method | Purpose | Application Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Steel Strapping | High-tensile strength; coil binding; structural integrity | Apply straps evenly spaced around the coil circumference, ensuring they are tight enough to prevent unwinding but not so tight as to damage the wire surface. Use edge protectors at strap points to prevent cutting into the packaging or wire. Consider cross-strapping for enhanced stability, especially for heavy or large diameter coils. Utilize appropriate tensioning and sealing tools for consistent and secure strapping. |
| Steel Banding | Robust coil containment; heavy-duty bundling | Employ heavy gauge banding for large, heavy coils requiring maximum containment. Apply banding with sufficient tension to create a rigid, unified coil package. Use multiple bands spaced appropriately to distribute pressure evenly. Consider rust-resistant or coated banding for coils exposed to marine or humid environments. Secure band ends with robust clips or seals designed for heavy-duty applications. |
| Reinforced Strapping Tape | Secure overlapping wraps; edge reinforcement; supplemental binding | Apply reinforced tape over stretch film or VCI paper wraps, particularly at coil edges and overlaps, to enhance tear resistance and seal integrity. Use in conjunction with steel strapping or banding for added security, especially for lighter coils. Select tape width and strength appropriate for coil size and weight. Ensure tape adhesion is effective under varying temperature and humidity conditions. Overlap tape layers significantly for maximum strength. |
Outer Packaging and Handling
The outermost layer is about ensuring ease of handling and providing final protection against external elements.
| Element | Purpose | Application Best Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Wooden Skids/Pallets | Base support; forklift handling; weight distribution | Select skid/pallet size and strength appropriate for coil dimensions and weight, ensuring adequate overhang to prevent tipping. Secure coil to skid/pallet using steel strapping or banding, ensuring even weight distribution. Use corner boards or chocks to further stabilize the coil and prevent shifting. Consider heat-treated pallets for international shipments to comply with ISPM 15 standards. |
| Corner Boards | Edge protection for wraps; reinforcement for stacking | Position corner boards under strapping or banding at coil edges to prevent cutting or crushing of inner wraps. Use heavy-duty corner boards for stacking to distribute weight and enhance package rigidity. Secure corner boards firmly to the coil and skid/pallet to prevent displacement during handling. Select corner board material (cardboard, plastic, or metal) based on required protection level and environmental conditions. |
| Weatherproof Shroud | Ultimate weather protection; UV protection; containment of loose ends | Enclose the entire coil package with a heavy-duty, UV-resistant, and waterproof shroud. Secure shroud tightly around the base of the skid/pallet to prevent water ingress from below. Overlap shroud edges and seal seams with waterproof tape for maximum weather resistance. Consider adding desiccant packets under the shroud for long-duration shipments in humid conditions. Ensure shroud material is compatible with steel and other packaging materials used. |
By carefully considering these techniques and tailoring them to the specific characteristics of the steel wire and the anticipated transportation hazards, optimal packaging solutions can be achieved, minimizing damage and ensuring customer satisfaction.
4. Step-by-Step Guide to Packaging Steel Wire
While theoretical knowledge of materials and methods is crucial, a practical, step-by-step approach ensures consistent and effective packaging of steel wire. This guide outlines a standardized procedure that can be adapted to various types and sizes of steel wire coils, promoting best practices across operations.
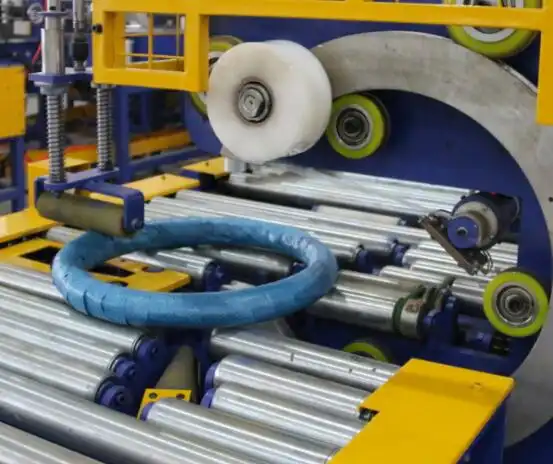

A systematic approach to packaging steel wire is essential for consistent quality and damage prevention. The process begins with material preparation, ensuring wire coils are clean and dry. Core wrapping follows, utilizing VCI paper or stretch film for corrosion protection. Coil wrapping involves applying steel straps or bands for structural integrity. Outer packaging on wooden skids or pallets provides a stable base, while corner boards and weatherproof shrouds add further protection. Labeling and documentation are the final steps, ensuring regulatory compliance and proper handling instructions throughout transportation.
This step-by-step guide will provide a practical framework for ensuring each steel wire shipment is packaged to withstand the challenges of transportation, from the factory floor to the customer’s doorstep.