What Are the Main Components of Mold Upenders?
Mold upenders are indispensable machinery in industries requiring the manipulation of heavy molds. These machines enhance safety and efficiency by automating the process of rotating molds. Understanding their core components is crucial for operation and maintenance.
Mold upenders are composed of several key components working in concert: the robust frame providing structural support, a powerful motor for rotation, an intelligent control system for precise operation, and critical safety features. Each component is integral to the upender’s functionality, ensuring safe and efficient mold handling.
This article delves into the essential components of mold upenders, explaining their functions and significance in ensuring seamless and safe mold handling operations. Grasping these details is vital for optimizing performance and extending the lifespan of your equipment.
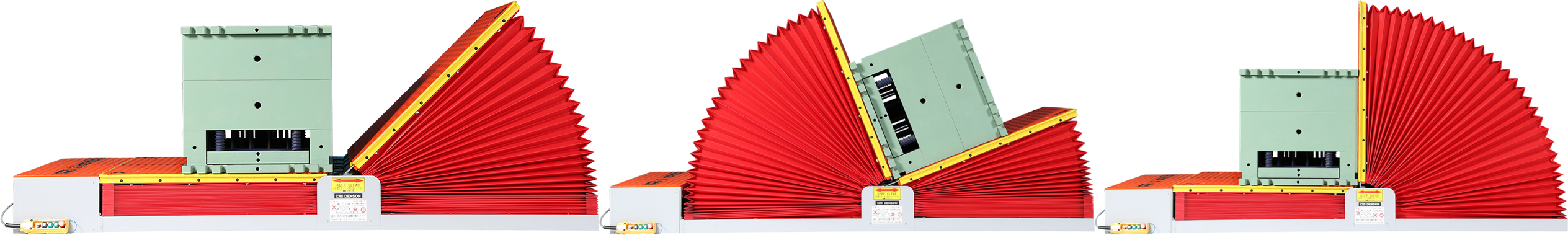
1. Frame: The Indispensable Backbone of Mold Upenders
The frame is the foundational element of any mold upender. It provides the necessary structural integrity to support heavy molds during lifting and rotation. A well-designed frame ensures stability and durability for demanding industrial applications.
The frame of a mold upender is the primary structural component, constructed from high-grade steel to bear immense weight. It is engineered to distribute load evenly, ensuring stability and preventing stress concentration. Its robust design minimizes wear and tear, contributing to the machine’s longevity and operational safety. Regular inspection is crucial to maintain its integrity and ensure continued safe operation.
Frame Analysis: Ensuring Structural Integrity and Longevity
The frame is more than just a base; it’s the skeletal system of the mold upender. Its design and material composition dictate the machine’s load-bearing capacity, stability, and overall lifespan. A poorly designed frame can lead to catastrophic failures, jeopardizing both equipment and personnel. Therefore, a detailed analysis of frame attributes is essential when considering a mold upender purchase or during routine maintenance checks. Let’s break down the key aspects:
Material Composition: High-Grade Steel and Beyond
The choice of material for the frame is paramount. High-grade steel is the industry standard due to its exceptional strength and durability. However, not all steels are created equal. Factors like yield strength, tensile strength, and fatigue resistance are crucial. For extremely heavy-duty applications, specialized steel alloys might be employed to enhance performance and safety margins. The selection process should always consider the maximum load capacity and the operational environment.
Design Engineering: Distributing Weight and Minimizing Stress
Effective frame design goes beyond just material selection. Engineers use sophisticated CAD and FEA software to model and simulate stress distribution across the frame under maximum load. The goal is to ensure even weight distribution and eliminate stress concentration points that could lead to cracks or deformation over time. Reinforcements, gussets, and strategically placed welds are all design elements that contribute to a frame’s robustness and longevity.
Load Capacity and Safety Factors: Built to Withstand Overload
Load capacity isn’t just about the maximum weight the upender can lift; it’s about the weight it can lift safely and reliably over its operational lifespan. Safety factors are incorporated into the design, meaning the frame is engineered to withstand loads significantly exceeding the stated capacity. This buffer is crucial for handling dynamic loads, unexpected weight shifts, and ensuring safety in demanding industrial environments.
Maintenance and Inspection: Preserving Frame Integrity
Even the most robust frame requires regular inspection and maintenance. Welds should be checked for cracks, and the entire structure should be examined for signs of corrosion or fatigue. Non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic testing, can be employed to assess the internal integrity of the steel without causing damage. Proactive maintenance is key to preventing costly repairs and ensuring the long-term safety and reliability of the mold upender.
| Attribute | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Typically high-grade steel; alloys for extreme loads | Determines strength, durability, and resistance to fatigue |
| Design | Engineered for even weight distribution; FEA analysis to minimize stress | Ensures stability, prevents deformation, and maximizes structural integrity |
| Load Capacity | Rated capacity with built-in safety factors | Guarantees safe operation even under dynamic loads and unexpected weight shifts |
| Maintenance | Regular inspections for welds, corrosion, fatigue; Non-destructive testing | Preserves structural integrity, prevents failures, and extends the lifespan of the frame |
By meticulously considering these aspects of the frame, manufacturers and operators can ensure the selection and maintenance of a mold upender that provides not only efficient operation but also unparalleled safety and long-term value. Remember, the frame is the silent workhorse, and its integrity is non-negotiable for safe and productive mold handling.
2. Electrical System: Powering Efficiency and Precision
The electrical system is the nerve center of a modern mold upender. It dictates the precision, speed, and overall efficiency of mold handling operations. Advanced electrical components enable seamless control and integration into automated workflows.
The electrical system in a mold upender is critical for providing precise control and efficient operation. It powers the motor, manages safety interlocks, and integrates control panels. Modern systems offer variable speed controls, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and seamless integration with existing manufacturing systems, enhancing both productivity and energy efficiency.
Advanced Electrical Systems: Driving Operational Excellence
The evolution of electrical systems in mold upenders has revolutionized mold handling. Gone are the days of cumbersome manual controls and inefficient energy consumption. Today, sophisticated electrical systems are at the heart of these machines, offering a range of benefits that directly impact productivity, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Let’s explore the key advancements:
Precision Control: Inverters and Variable Speed Drives
Modern mold upenders utilize inverters and variable speed drives to achieve unparalleled control over motor speed and torque. This allows for smooth starts and stops, preventing sudden jolts that could damage molds or create safety hazards. Variable speed control also optimizes cycle times, allowing operators to adjust the rotation speed based on the specific mold being handled.
Seamless Integration: PLCs and Automation
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are the brains behind many advanced mold upender electrical systems. PLCs enable seamless integration with other automated systems in a manufacturing facility. They can be programmed to execute complex sequences, interface with sensors and safety devices, and even communicate with central management systems for data logging and remote monitoring. This level of integration is crucial for achieving Industry 4.0 compatibility and optimizing overall workflow automation.
Energy Efficiency: Regenerative Braking and Smart Power Management
Modern electrical systems are designed with energy efficiency in mind. Features like regenerative braking capture energy during deceleration and feed it back into the system, reducing overall power consumption. Smart power management systems optimize energy usage based on load and operational demands, further contributing to cost savings and environmental sustainability.
Diagnostic Capabilities: Minimizing Downtime
Advanced electrical systems often incorporate diagnostic capabilities that can significantly reduce downtime. These systems can monitor system performance, detect potential faults, and provide real-time alerts to operators or maintenance personnel. This proactive approach to maintenance allows for timely intervention, preventing minor issues from escalating into major breakdowns and keeping production running smoothly.
By embracing these advancements in electrical systems, manufacturers can unlock significant improvements in mold upender performance, efficiency, and reliability. The investment in sophisticated electrical components translates directly into enhanced productivity, reduced operational costs, and a safer working environment.
3. Safety Features: Prioritizing Operator and Equipment Protection
Safety features are non-negotiable components in mold upenders and mold turning machinery. They are paramount for protecting personnel, preventing accidents, and ensuring the longevity of the equipment itself. Robust safety systems are an investment in operational continuity and workplace well-being.
Safety features are absolutely essential in mold upenders to mitigate risks associated with handling heavy molds. Emergency stops, light curtains, safety interlocks, and overload protection systems are critical. These features protect operators from potential injury, prevent equipment damage due to misuse or malfunction, and contribute to a safer and more productive work environment.
Essential Safety Mechanisms: A Multi-Layered Approach
Safety in mold handling is not a single feature but a comprehensive system encompassing multiple layers of protection. Modern mold upenders are equipped with a range of safety mechanisms, each designed to address specific potential hazards. A multi-layered approach ensures redundancy and provides a robust safety net for operators and equipment. Let’s examine some of the most critical safety features:
Emergency Stop Systems: Immediate Shutdown in Critical Situations
Emergency stop buttons are strategically placed around the mold upender, allowing for immediate shutdown in case of any unsafe condition or emergency. These systems are designed for quick and easy activation, ensuring that operation can be halted instantly to prevent accidents or damage. Reliable emergency stop systems are a fundamental safety requirement for all industrial machinery.
Light Curtains and Safety Scanners: Perimeter Protection
Light curtains and safety scanners create invisible safety zones around the operational area of the mold upender. If an operator or any object breaches these zones during operation, the machine automatically stops. Light curtains are ideal for guarding access points, while safety scanners can provide wider area protection, especially in automated setups. These systems prevent accidental intrusion into hazardous zones, safeguarding personnel from potential crush injuries.
Safety Interlocks: Preventing Operation in Unsafe Conditions
Safety interlocks are designed to prevent machine operation if certain safety conditions are not met. For example, interlocks can ensure that safety gates are closed and locked before the upender can start operating. They can also monitor for overload conditions or other system malfunctions, preventing operation if any unsafe parameters are detected. Safety interlocks are crucial for ensuring that the machine operates only in a safe and controlled manner.
Overload Protection: Safeguarding Against Excessive Loads
Overload protection systems monitor the weight being lifted by the mold upender and prevent operation if the load exceeds the machine’s rated capacity. These systems typically use load cells or other sensing devices to detect excessive loads and trigger an automatic stop. Overload protection prevents damage to the machine’s structural components and hydraulic or electrical systems, extending its lifespan and preventing potential failures.
| Safety Feature | Functionality | Operational Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency Stop | Immediate shutdown upon detecting unsafe conditions | Prevents accidents, minimizes damage, ensures rapid response to emergencies |
| Light Curtains | Sensors preventing intrusion into the operational zone | Safeguards operators from entering hazardous areas, prevents crush injuries |
| Safety Interlocks | Prevents operation under unsafe conditions (e.g., open safety gates) | Ensures safe and predictable operation, reduces risk of human error |
| Overload Protection | Detects and stops operation if exceeding safe load limits | Prevents equipment damage, extends machine lifespan, avoids structural failures |
Investing in comprehensive safety features is not just about compliance; it’s about creating a culture of safety in the workplace. These features not only protect operators from harm but also contribute to increased productivity by minimizing downtime due to accidents and ensuring smooth, uninterrupted operations. A safe working environment is a productive working environment.
4. Customization: Tailoring Mold Upenders to Specific Needs
Mold upenders are not one-size-fits-all machines. Customization is a key aspect, allowing these machines to be tailored to the specific demands of different industries and applications. From size and capacity to specialized controls, customization ensures optimal performance and integration.
Customization is vital for mold upenders to meet diverse industrial needs. Options include adjusting payload capacity, platform size, tilting angles (90°, 180°, 360°), and control systems. Customization ensures the upender seamlessly integrates into existing workflows, optimizes efficiency for specific mold types and sizes, and enhances overall operational effectiveness.
Mold upender customization is a collaborative process, often involving close consultation between the manufacturer and the client. Understanding the specific application, workflow, and environmental conditions is crucial for designing a machine that perfectly meets the client’s needs. Here are some key areas where customization plays a significant role:
- Payload Capacity: Upenders can be designed to handle a wide range of mold weights, from a few tons to hundreds of tons. Customizing the payload capacity ensures that the machine is robust enough for the heaviest molds while remaining efficient for lighter loads.
- Platform Size and Type: The dimensions of the rotating platform can be customized to accommodate different mold sizes and shapes. Platform surfaces can also be tailored, with options like steel, wood, or rollers, depending on the specific handling requirements.
- Tilting Angle: While 90° tilting is common, upenders can be customized for 180° or even 360° rotation, depending on the application. Die splitters, for example, often require 180° rotation for complete mold separation.
- Control Systems: Control systems can range from simple pendant panels to advanced automated systems integrated with the plant’s WMS/ERP. Customization can include remote controls, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and Industry 4.0 compatibility features.
- Safety Features: While standard safety features are essential, customization can involve adding specialized safety devices like laser scanners for hazardous area protection or integrating with existing plant safety systems.
- Operating Environment: Upenders can be customized for specific operating environments, including indoor, outdoor, and even hazardous areas (ATEX/IECEx certified) with explosion-proof components.
By leveraging customization options, businesses can acquire mold upenders that are perfectly aligned with their unique operational requirements, maximizing efficiency, safety, and long-term return on investment.
Conclusion
Understanding the main components of mold upenders is crucial for optimizing manufacturing workflows and ensuring safe and efficient mold handling. From the robust frame to the precision electrical systems, critical safety features, and tailored customization, each component plays a vital role in the overall performance and reliability of these essential machines. This knowledge empowers engineers, technicians, and operators to make informed decisions regarding operation, maintenance, and selection, ultimately enhancing productivity and safety in mold handling applications.
