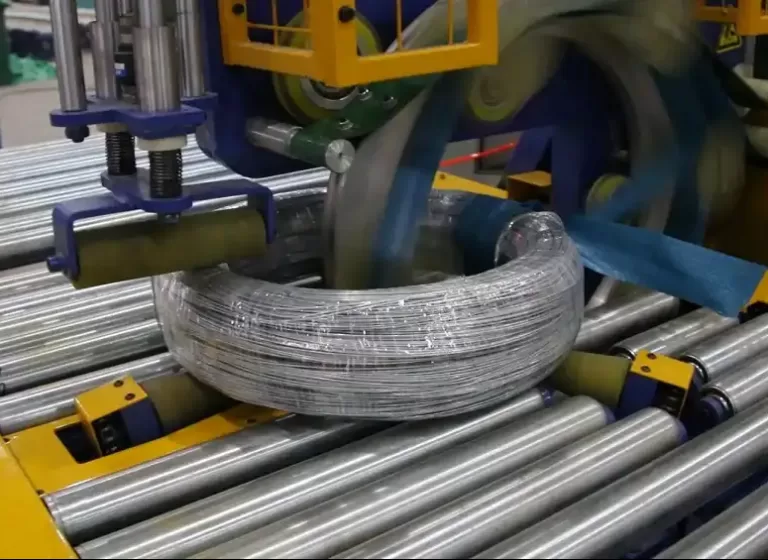
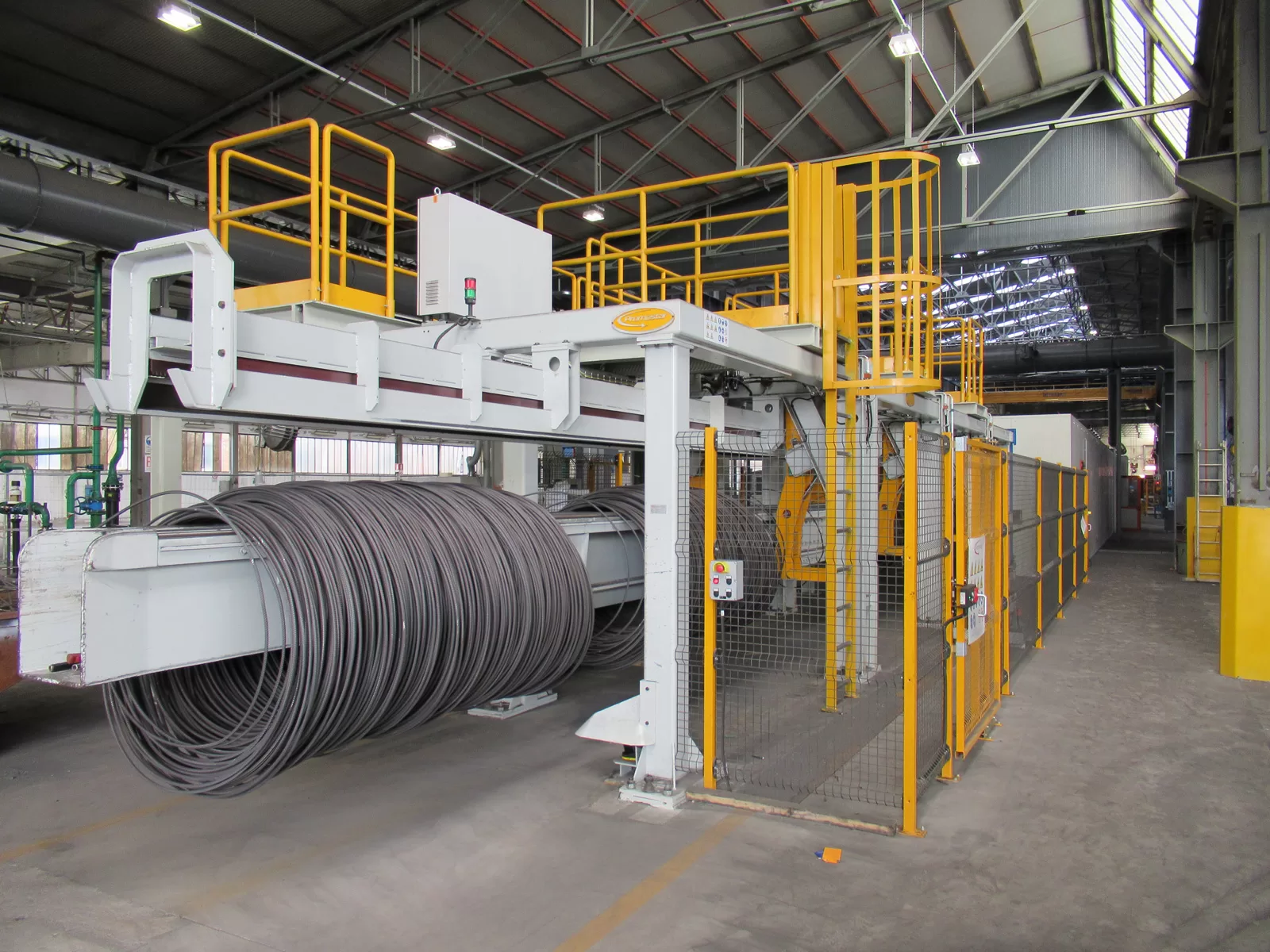
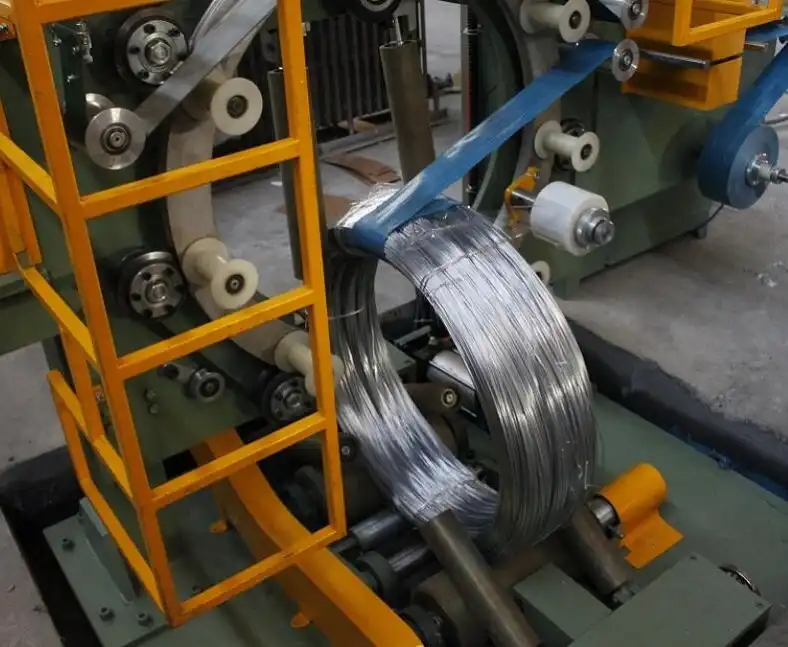
Steel wire packing is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient transportation and storage of steel wire products. The materials used in this process must possess specific characteristics to protect the wire from damage, corrosion, and environmental factors. Choosing the right packing material is essential for maintaining the integrity of the steel wire from production to end-use.
The primary characteristics of materials used in steel wire packing are durability, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness. These materials, such as PVC wrap, HDPE sheets, and paper wrap, each offer different levels of protection and environmental impact. Selecting the optimal material involves balancing these characteristics with the specific needs of the steel wire being packed and the overall logistical requirements.
Selecting the correct materials for steel wire packing is not just about containment; it’s about optimizing protection, cost, and sustainability. Let’s delve into the essential characteristics and material options that define effective steel wire packing.

2. Durability and Protection in Steel Wire Packing Materials
Durability is paramount when selecting materials for steel wire packing. These materials must withstand the rigors of handling, transportation, and storage, ensuring the steel wire remains undamaged and protected. The level of durability required often depends on the type of steel wire, its intended use, and the expected environmental conditions during transit and storage.
Durable materials for steel wire packing, like HDPE sheets and PVC wrap, offer high tensile strength and resistance to tearing and puncture. This robustness is crucial for preventing physical damage to the steel wire, such as scratches, bends, or breaks, which can compromise its quality and usability. Paper wrap, while less durable, can provide a basic level of surface protection for lighter-duty applications or when combined with other materials.
To understand the nuances of durability in steel wire packing, we need to consider various factors and material properties. Let’s break down the critical aspects of durability and explore how different materials measure up.
Assessing Material Strength for Steel Wire Protection
The strength of a packing material is not a singular property but encompasses several aspects that contribute to its overall durability. For steel wire packing, key strength characteristics include tensile strength, tear resistance, and puncture resistance.
-
Tensile Strength: This measures a material’s resistance to breaking under tension or pulling forces. High tensile strength is vital for materials that will be stretched or tightly wrapped around steel wire coils, ensuring they don’t snap or lose integrity during application or transit.
-
Tear Resistance: This indicates a material’s ability to resist tearing once a tear has been initiated. Materials with good tear resistance are less likely to propagate tears from minor abrasions or punctures, maintaining their protective barrier.
-
Puncture Resistance: This measures a material’s ability to withstand sharp objects without being pierced. For steel wire packing, puncture resistance is crucial to protect against damage from handling equipment, sharp edges of the wire itself, or debris during transportation.
To illustrate how different materials compare in these strength aspects, consider the following table:
| Material | Tensile Strength | Tear Resistance | Puncture Resistance | Overall Durability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC Wrap | High | Medium | Medium | High |
| HDPE Sheets | Very High | High | High | Very High |
| Paper Wrap | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Steel Banding | Very High | Very High | Very High | Very High |
As the table shows, HDPE sheets offer superior durability across all strength aspects, making them ideal for heavy-duty steel wire packing. PVC wrap provides a good balance of strength and cost-effectiveness, while paper wrap is suitable for less demanding applications where basic surface protection is sufficient. Steel banding, although not a wrap, offers the highest level of strength and is used for securing heavy coils. The choice depends on the specific durability needs of the steel wire being packaged.

3. Moisture Resistance and Corrosion Prevention in Steel Wire Packing
Moisture resistance is another critical characteristic for steel wire packing materials. Steel is susceptible to corrosion, especially in humid or wet environments. Packing materials must effectively prevent moisture ingress to maintain the quality and integrity of the steel wire during storage and transportation. Material characteristics play a pivotal role in ensuring long-term protection against rust and degradation.
Materials like PVC and HDPE are inherently water-resistant and provide excellent barriers against moisture. They prevent water from reaching the steel wire, thus minimizing the risk of rust and corrosion. Paper wrap, on the other hand, offers minimal moisture resistance and is generally unsuitable for long-term storage or exposure to humid conditions unless treated or combined with moisture barrier layers.
Let’s delve deeper into the importance of moisture resistance and explore how different materials perform in preventing corrosion in steel wire.
The Science of Moisture Barriers in Wire Packing
The effectiveness of a packing material in preventing corrosion hinges on its ability to act as a moisture barrier. This barrier function is determined by the material’s inherent properties and its structural integrity when applied as packaging.
-
Water Absorption: Materials that absorb water can trap moisture against the steel wire, paradoxically increasing the risk of corrosion. Ideal packing materials should be non-absorbent or have very low water absorption rates.
-
Water Vapor Permeability: This measures how easily water vapor can pass through a material. Low water vapor permeability is essential to prevent moisture from the surrounding environment from reaching the steel wire, even if the packaging is not directly exposed to liquid water.
-
Sealing Integrity: Even highly moisture-resistant materials can fail if the packaging seals are compromised. Proper sealing techniques and material compatibility at seams and overlaps are crucial for maintaining a continuous moisture barrier.
Consider this comparison of moisture resistance properties for common steel wire packing materials:
| Material | Water Absorption | Water Vapor Permeability | Sealing Integrity | Corrosion Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVC Wrap | Very Low | Low | Good | Excellent |
| HDPE Sheets | Negligible | Very Low | Excellent | Excellent |
| Paper Wrap | High | High | Poor | Poor |
| Treated Paper | Low to Medium | Medium to Low | Fair to Good | Fair to Good |
PVC and HDPE again stand out for their superior moisture barrier properties. Their negligible water absorption and low water vapor permeability make them highly effective in preventing corrosion. Paper wrap, in its standard form, is inadequate for moisture-sensitive steel wire. However, treated paper, with coatings or laminations, can offer improved moisture resistance for less demanding applications. The sealing method used also greatly impacts the overall moisture protection, with heat sealing generally providing better integrity than taping or adhesives for plastic wraps.

4. Cost-Effectiveness and Material Selection for Steel Wire Packing
Cost-effectiveness is a significant consideration in material selection for steel wire packing. While durability and protection are crucial, the chosen materials must also be economically viable, especially for large-scale industrial applications. Balancing performance with cost is key to optimizing the overall packaging strategy.
Paper wrap is generally the most cost-effective option, offering a low initial material cost. However, its limited durability and moisture resistance may necessitate additional protective measures or result in higher rates of damage and waste, potentially increasing overall costs. PVC and HDPE wraps are more expensive upfront but offer superior protection, potentially reducing product loss and long-term expenses related to damage and corrosion.
Let’s analyze the cost implications and explore strategies for achieving cost-effective steel wire packing without compromising essential protection.
Balancing Cost and Performance in Wire Packaging
Achieving cost-effectiveness in steel wire packing involves a holistic approach that considers not just the material cost per unit but also factors like material usage, labor costs, damage rates, and disposal expenses.
-
Material Cost vs. Usage: While paper wrap may have a lower per-unit cost, it might require more layers or additional reinforcement to achieve adequate protection compared to HDPE or PVC. This increased usage can negate some of the initial cost savings. Conversely, while HDPE is more expensive per unit, its superior strength might allow for thinner wraps, reducing the total material used per coil.
-
Labor and Automation: The ease of application of packing materials impacts labor costs. PVC and HDPE wraps are well-suited for automated wire packing machines, reducing labor intensity and increasing throughput. Paper wrap, especially for complex coil shapes, might be more labor-intensive to apply effectively.
-
Damage and Waste Reduction: Investing in more robust and protective materials like HDPE or PVC can significantly reduce damage rates during transit and storage. Lower damage translates to less product waste, fewer returns, and enhanced customer satisfaction, all contributing to long-term cost savings.
-
Disposal and Recycling Costs: Environmental regulations and disposal costs are increasingly important. Paper wrap is often easier and cheaper to recycle than PVC, although HDPE is also recyclable in many regions. Considering the end-of-life disposal costs and potential revenue from recycling can influence the overall cost-effectiveness of different material choices.
To illustrate the cost-performance trade-offs, consider this comparative cost analysis:
| Material | Material Cost (per unit) | Material Usage | Labor Cost (Application) | Damage Rate | Disposal Cost | Overall Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper Wrap | Low | High | Medium | High | Low | Medium |
| PVC Wrap | Medium | Medium | Low | Medium | Medium | Medium to High |
| HDPE Sheets | High | Low | Low | Low | Medium | High |
HDPE sheets, despite higher material costs, can be the most cost-effective in the long run due to lower material usage, reduced labor with automation, and minimal damage rates. PVC wrap offers a good balance, while paper wrap’s initial cost savings may be offset by higher usage, labor, and damage rates, especially for demanding applications. A thorough cost analysis, considering all these factors, is crucial for making informed material choices in steel wire packing.
Conclusion
Selecting the right materials for steel wire packing involves a careful evaluation of durability, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Materials like HDPE and PVC offer superior protection and longevity, while paper provides a more economical option for less demanding applications. The ideal choice hinges on balancing these characteristics to meet the specific needs of the steel wire product and the logistical environment, ensuring both product integrity and economic efficiency. Ultimately, effective steel wire packing is a blend of material science, practical application, and strategic cost management.