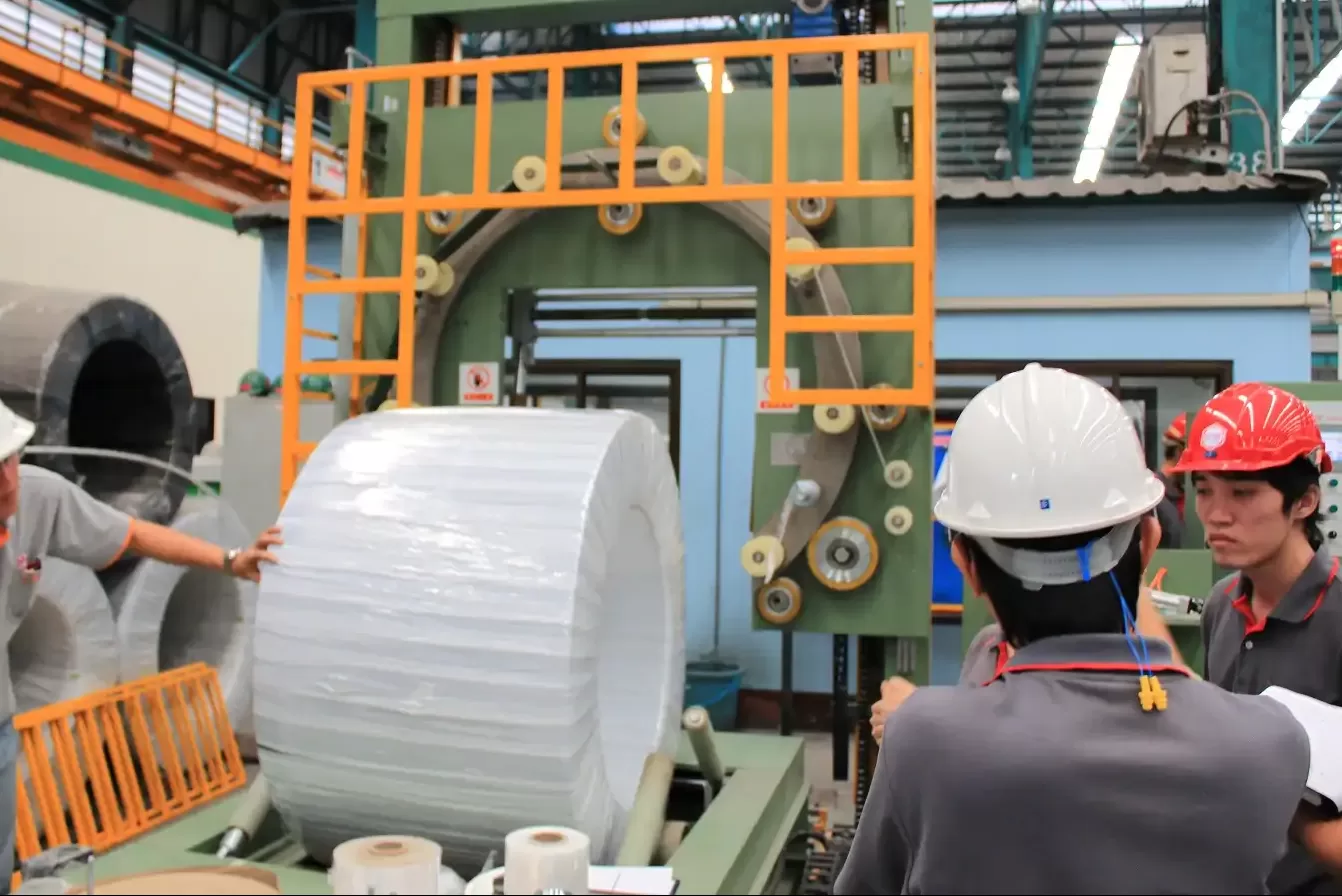
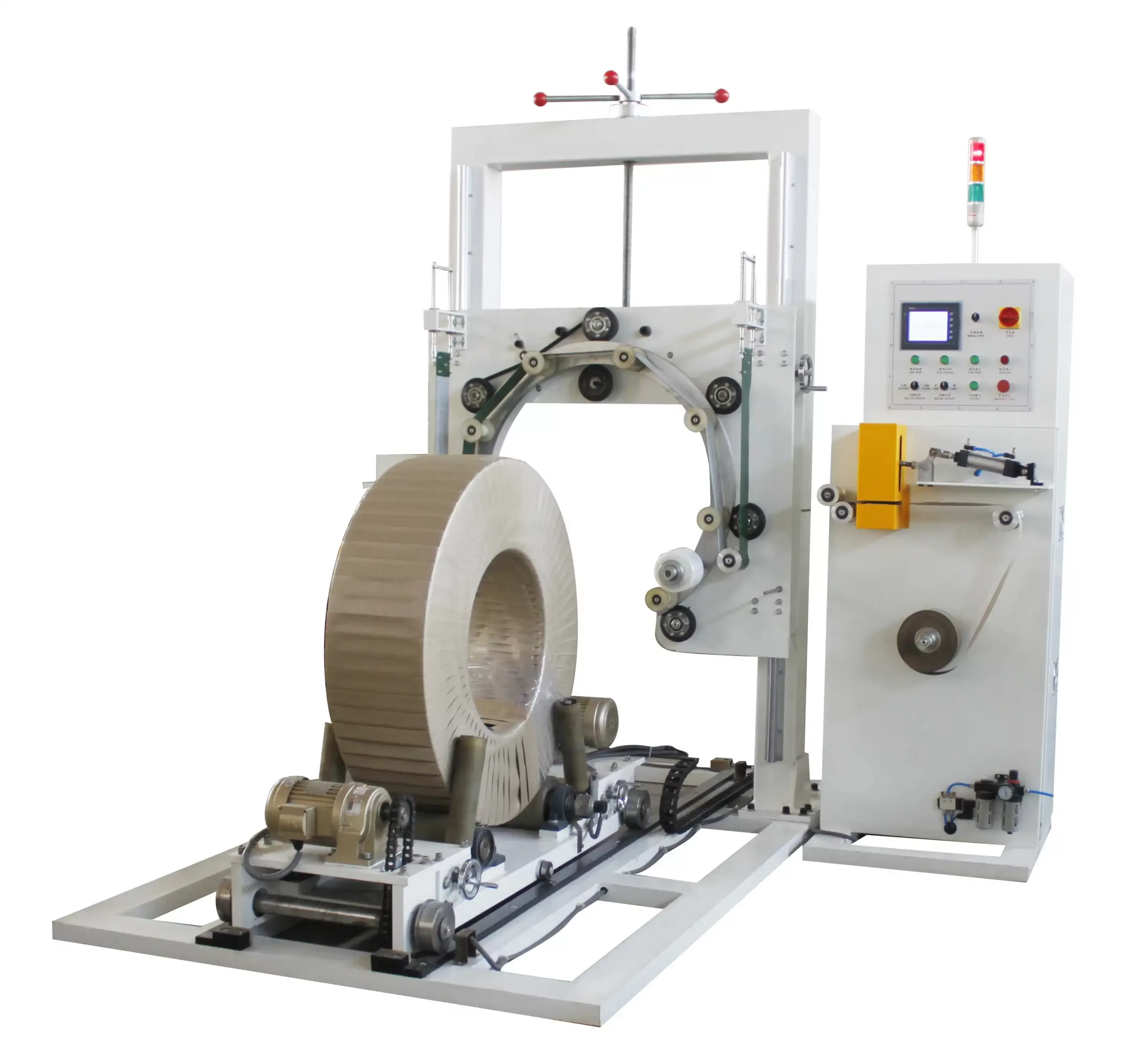
1. How to Improve Shock Resistance in Steel Wire Packing?
Steel wire packing is crucial for ensuring products arrive safely. However, these dense coils are vulnerable to shocks during transit. Enhancing shock resistance in steel wire packing protects the wire, reduces damage, and maintains product integrity. This article explores effective strategies to improve shock resistance and safeguard your steel wire shipments.

To improve shock resistance in steel wire packing, focus on robust packaging design, material selection, and protective features. Utilize cushioning materials like foam or corrugated cardboard, implement multi-layered packaging, and consider features like shock indicators to monitor handling. Proper strapping and securing within the package are also essential for minimizing movement and absorbing impact.
Effective steel wire packing is not merely about containing the product; it’s about ensuring its journey is as safe as its production. Let’s delve into the methods and materials that can significantly enhance shock resistance in steel wire packing, safeguarding your valuable steel wire coils from damage.
2. Selecting the Right Packaging Materials for Impact Protection
Choosing the correct materials is the foundation of impact protection in steel wire packing. The materials must withstand the rigors of handling and transportation, providing a buffer against shocks and vibrations. Selecting materials with inherent shock-absorbing qualities is paramount for minimizing damage.
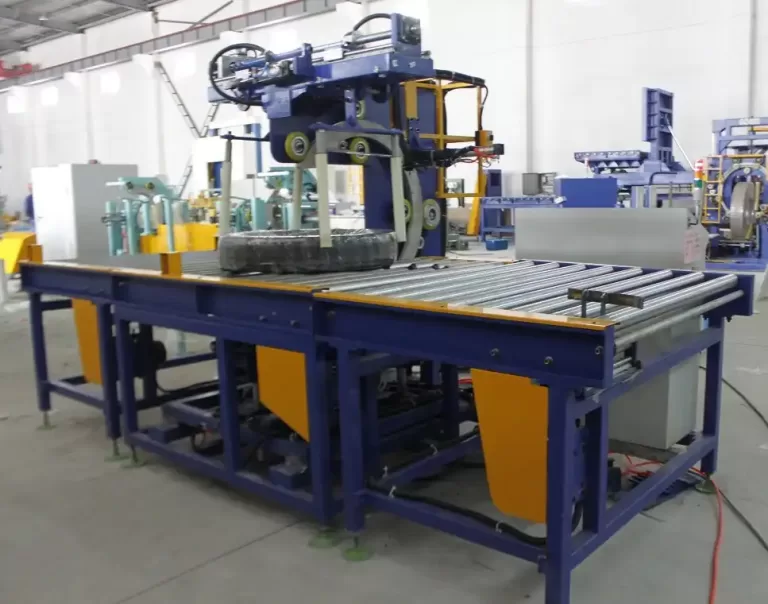

For optimal impact protection, steel wire packing should utilize a combination of materials. Start with a sturdy base like wooden pallets or skids. Employ cushioning materials such as high-density foam, corrugated cardboard, or even air pillows to absorb shocks. Outer layers should consist of durable materials like thick plastic films or steel strapping to contain and further protect the wire coil from external impacts.
Analyzing Cushioning Material Performance
The effectiveness of cushioning materials is not uniform; it varies based on material type, thickness, and the load it bears. Understanding these nuances is crucial for selecting the right cushioning for steel wire. Let’s examine how different materials perform under shock.
Material Performance Comparison
| Material Type | Cushioning Ability | Durability | Cost | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) | Excellent | Moderate | Low | Lightweight coils, minimal handling risks |
| Polyurethane Foam | Very Good | Moderate | Medium | Medium-weight coils, moderate handling risks |
| Corrugated Cardboard | Good | Good | Low | Medium to heavy coils, general protection |
| Wood Wool | Moderate | Good | Medium | Heavy coils, robust protection needed |
| Air Pillows | Fair | Low | Low | Light coils, void fill, supplementary cushioning |
As the table illustrates, EPS offers excellent cushioning but may lack durability for heavy steel wire. Corrugated cardboard provides a balanced approach, while wood wool is suited for the heaviest applications demanding maximum impact protection. The choice depends heavily on the wire coil’s weight, fragility, and the anticipated transportation conditions.
3. Designing Packaging for Enhanced Shock Absorption
Beyond material selection, packaging design plays a critical role in shock absorption. A well-designed package distributes impact forces, minimizing stress concentration on the steel wire. This involves structural considerations and incorporating specific design elements to enhance protection.
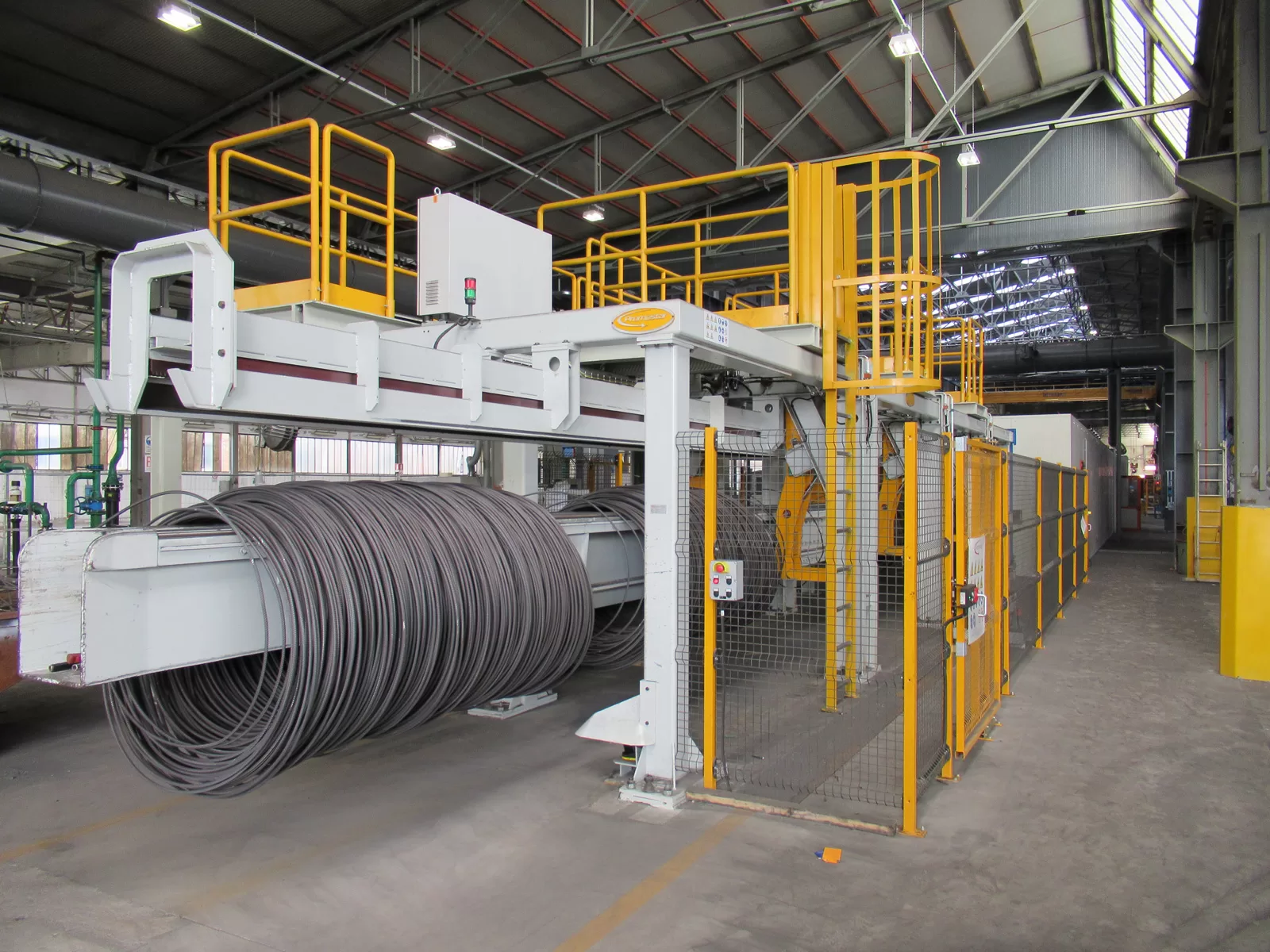

Effective packaging design for shock absorption incorporates several key features. Multi-layered construction is crucial, combining cushioning and rigid layers. Internal supports and dividers prevent coil shifting and distribute weight evenly. External strapping reinforces the structure, while rounded corners on the outer packaging can deflect impacts. The goal is to create a package that acts as a unified, shock-absorbing system.
Advanced Packaging Design Techniques
To further enhance shock absorption, consider these advanced design techniques that go beyond basic layering and strapping. These methods are particularly useful for highly sensitive or heavy steel wire coils where standard packaging might fall short.
Implementing Advanced Design Features
| Design Feature | Function | Benefit | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Floating Platforms | Suspend coil within outer packaging | Isolates coil from direct impacts on the outer box | Delicate wires, sensitive coatings |
| Corner and Edge Reinforcements | Strengthen vulnerable points of the package | Prevents crushing and deformation during drops | Heavy coils, long-distance transport |
| Customized Inserts | Molded or fitted cushioning for coil shape | Ensures snug fit, prevents movement, maximizes cushioning effect | Coils with irregular shapes, high-value wires |
| Pre-compressed Cushions | Materials compressed before packaging | Provides consistent cushioning performance under load | Heavy coils, applications requiring predictable shock absorption |
| Wire packing machine Integration | Design packaging compatible with automated packing lines | Streamlines process, reduces manual handling, improves consistency | High-volume production, automated warehouses |
These advanced features, especially floating platforms and customized inserts, offer superior shock absorption by precisely controlling the coil’s movement and maximizing the cushioning material’s effectiveness. Integrating packaging design with automated wire packing machine systems can further enhance efficiency and reduce handling-related shocks.
4. Protective Features: Beyond Basic Packaging
While materials and design form the core of shock-resistant packing, additional protective features act as supplementary safeguards. These features can range from simple additions like edge protectors to sophisticated shock monitoring devices. They provide an extra layer of assurance, particularly for sensitive steel wire shipments.
Protective features for steel wire packing include edge protectors, corner boards, and stretch wrap to reinforce structural integrity. Shock indicators are crucial for monitoring handling during transit, alerting recipients to potential impacts. Vibration dampeners can be incorporated for long journeys, and rust inhibitors protect against environmental factors. These features collectively enhance the package’s ability to withstand and indicate mishandling.
Integrating Shock Monitoring and Indicators
A significant advancement in protective features is the use of shock indicators and monitoring devices. These tools provide real-time or post-transit information about the shocks experienced by the package, allowing for accountability and process improvement.
Types of Shock Monitoring Devices
| Device Type | Functionality | Sensitivity Levels | Cost | Usage Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shock Indicators | Visual indication of impact exceeding threshold | Pre-set G-levels | Low | General shipments, basic monitoring |
| Shockwatch Labels | Tamper-proof visual indicators | Various G-levels | Low to Medium | Sensitive goods, accountability for handling |
| ShockDot Indicators | Cost-effective, wide range of sensitivities | Broad G-level range | Low | Cost-sensitive shipments, varied fragility levels |
| Omni-G Indicators | Resettable, reusable impact detectors | Adjustable G-levels | Medium | Reusable packaging, internal transport |
| Data Loggers | Record time, magnitude, and duration of shocks | Programmable | High | High-value shipments, detailed impact analysis |
Shock indicators like Shockwatch labels offer immediate visual confirmation of mishandling. For more detailed analysis, data loggers provide a comprehensive record of shock events during transit. Choosing the right device depends on the value of the steel wire, the sensitivity to shock, and the level of monitoring required.
5. Testing and Validation of Shock Resistance
The final, critical step in improving shock resistance is rigorous testing and validation. Theoretical design and material selection are essential, but real-world testing confirms the packaging’s effectiveness. Testing simulates the shocks and stresses encountered during transportation, ensuring the packaging performs as intended.

Validating shock resistance requires standardized testing procedures. Drop tests from varying heights simulate handling impacts. Vibration tests assess package resilience during transit. Compression tests ensure structural integrity under stacking loads. Impact tests, both horizontal and inclined, mimic transportation shocks. These tests, often guided by ASTM or ISTA standards, provide quantifiable data on packaging performance.
Comprehensive Shock Resistance Testing Procedures:
Effective shock resistance in steel wire packing is achieved through a holistic approach encompassing material selection, design innovation, protective features, and rigorous testing. By implementing these strategies, businesses can significantly reduce damage, ensure product integrity, and optimize their steel wire shipping processes.
Conclusion
Improving shock resistance in steel wire packing is a multifaceted process that significantly impacts product safety and customer satisfaction. By carefully selecting materials, implementing advanced packaging designs, incorporating protective features like shock indicators, and rigorously testing packaging performance, manufacturers can ensure their steel wire coils arrive at their destination in optimal condition. This comprehensive approach minimizes damage, reduces costs associated with returns and replacements, and ultimately enhances the reliability and reputation of steel wire suppliers in the market.








