How to Implement a Mobile Design for Mold Upenders?
Implementing a mobile design for mold upenders revolutionizes heavy mold handling in manufacturing. By integrating mobility, these machines offer unparalleled flexibility and efficiency, adapting to dynamic production environments and optimizing workflow. This article explores the essential aspects of designing and implementing mobile mold upenders for enhanced operational agility.
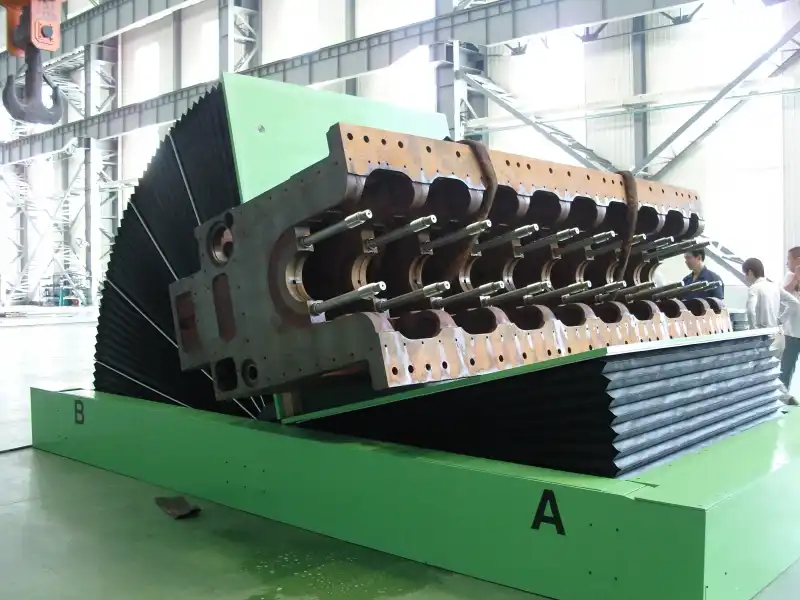

To implement a mobile design for mold upenders, focus on integrating robust wheels or casters, ensuring a compact and balanced structure for easy maneuverability, and incorporating safety mechanisms like brakes and locking systems. Power options such as battery-powered hydraulics or towable configurations further enhance mobility, allowing seamless relocation and adaptation to diverse factory layouts.
Transitioning to mobile mold upenders enhances operational flexibility and streamlines workflow. Let’s delve into the key considerations for designing and implementing these dynamic machines.
1. Key Considerations for Mobile Mold Upender Design
Designing mobile mold upenders requires a meticulous approach, balancing mobility with the robust functionality needed for heavy mold handling. Several crucial factors dictate the effectiveness and safety of these mobile systems, ensuring they meet the demands of dynamic industrial environments.
When designing mobile mold upenders, prioritize load capacity appropriate for the molds being handled, select durable and maneuverable wheel systems, integrate a stable and balanced structural design, and incorporate user-friendly controls that are accessible during mobile operation. Safety features like reliable braking systems, emergency stops, and secure locking mechanisms are also paramount to ensure safe relocation and operation in varied factory settings.
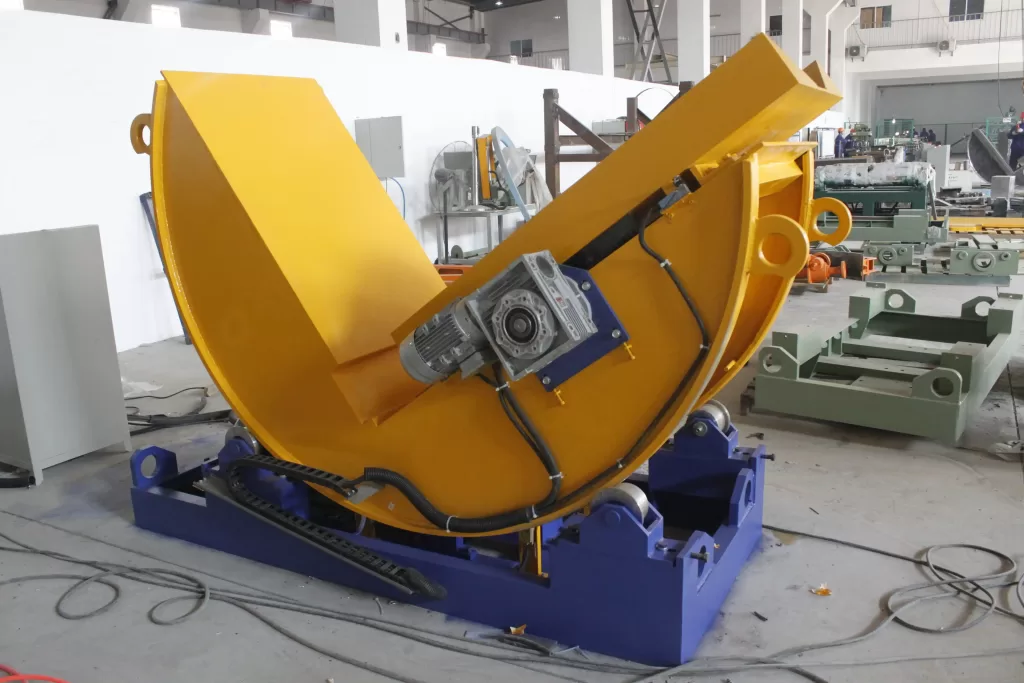

Balancing Mobility and Stability in Mobile Mold Upender Design
Mobile mold upenders inherently introduce a challenge: maintaining stability while enabling movement. A successful design requires carefully balancing these opposing needs. To achieve this, engineers must consider several critical elements:
Structural Integrity and Weight Distribution
The frame of a mobile mold upender needs to be exceptionally rigid to withstand both the static load of the mold and the dynamic stresses introduced during movement and upending operations. High-strength steel is typically the material of choice for the frame, ensuring durability and resistance to deformation. Crucially, weight distribution must be meticulously planned. A low center of gravity is essential to prevent tipping, especially when moving with a mold or during the tilting process. Components like hydraulic power packs and heavy structural elements should be positioned to contribute to this low center of gravity.
Wheel and Caster Systems
The selection of wheels or casters is paramount for mobility. Factors to consider include:
| Wheel Type | Load Capacity | Maneuverability | Floor Condition | Durability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solid Rubber | Medium | Good | Smooth | High | Medium |
| Pneumatic | High | Excellent | Uneven | Medium | High |
| Polyurethane | High | Good | Smooth | Very High | High |
| Steel | Very High | Fair | Smooth, Durable | Extremely High | High |
For heavy molds, polyurethane or steel wheels are often preferred due to their high load capacity and durability. Pneumatic wheels offer superior maneuverability over uneven surfaces but may require more maintenance and are susceptible to punctures. Swivel casters enhance maneuverability, allowing for changes in direction, but locking mechanisms are crucial to secure the upender in place during operation and prevent unintended movement.
Braking and Locking Systems
Effective braking and locking systems are non-negotiable safety features for mobile mold upenders. Brakes should be easily accessible and robust enough to hold the upender stationary, even on slight inclines and under full load. Both wheel brakes and swivel locks on casters should be implemented. Wheel brakes prevent rolling, while swivel locks prevent the casters from rotating, providing comprehensive immobilization. Emergency braking systems, perhaps automatically activated in case of power loss or operator error, can add an extra layer of safety.
By meticulously considering these aspects – structural integrity, weight distribution, wheel systems, and braking mechanisms – designers can create mobile mold upenders that are both highly maneuverable and exceptionally stable, ensuring safe and efficient mold handling in dynamic industrial environments.
2. Power and Mobility Options for Mold Upenders
Mobile mold upender designs offer diverse power and mobility configurations to suit various operational needs and factory layouts. Choosing the right power and mobility option is critical for optimizing efficiency and flexibility.
Power options for mobile mold upenders range from traditional electric and hydraulic systems to battery-powered solutions, each impacting mobility and operational range. Mobility itself is achieved through integrated wheel systems, towable designs, or even self-propelled mechanisms. Selecting the appropriate combination depends heavily on the intended use case, factory environment, and the scale of mold handling operations.
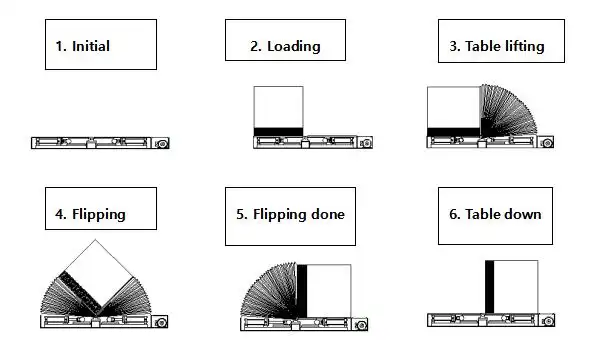
Exploring Power and Movement Technologies
The mobility of a mold upender is intricately linked to its power source and movement mechanism. Let’s explore the common options:
Power Source Options
-
Electric Hydraulic: This is a prevalent choice, combining the power of hydraulics for lifting and tilting with electric motors for operation. For mobile units, power can be supplied via trailing cables or, for greater mobility, battery packs. Battery-powered hydraulic systems are gaining popularity for mobile applications as they eliminate cable constraints, offering greater freedom of movement.
-
Pneumatic: Pneumatic systems utilize compressed air. While less common for very heavy mold upenders due to power limitations, they can be suitable for lighter applications. Pneumatic systems are generally simpler and can be advantageous in environments where electrical safety is a concern, but require a compressed air supply.
-
Manual Hydraulic: For smaller, lighter mold upenders, manual hydraulic systems offer a cost-effective and simple solution. These are operated via hand pumps and are ideal for situations where power sources are limited or for very occasional use. Mobility is typically manual pushing or towing.
Mobility Mechanisms
-
Integrated Wheel Systems: The most common mobility solution involves integrating wheels or casters directly into the mold upender’s frame. This can range from simple fixed wheels for straight-line movement to swivel casters for omnidirectional maneuverability. Larger diameter wheels are better for uneven floors, while smaller, harder wheels are suitable for smooth surfaces.
-
Towable Designs: For heavier mobile mold upenders, towable designs are practical. These units are equipped with a towing hitch and can be moved using a forklift or other industrial vehicle. Towable units often feature robust wheel and axle systems designed for heavier loads and potentially rougher terrain.
-
Self-Propelled Systems: For maximum maneuverability and independent movement, self-propelled mold upenders are available. These are typically battery-powered and incorporate drive wheels and steering mechanisms, allowing operators to precisely position the upender without external towing vehicles. These systems are more complex and costly but offer the highest degree of mobility and operational flexibility.
Choosing the optimal power and mobility combination depends on a detailed analysis of the operational environment, mold weights, required maneuverability, and budget. Factors like power availability, floor conditions, and frequency of relocation should all influence the selection process.
3. Safety and Operational Features of Mobile Designs
Safety is paramount in any mold handling operation, and mobile mold upenders require enhanced safety features due to their dynamic nature. Operational features must also be carefully considered to ensure ease of use and efficiency during mobile operation.
Mobile mold upenders incorporate crucial safety features such as emergency stop buttons readily accessible during movement, proximity sensors to prevent collisions, and audible and visual alarms to signal operation. Operationally, mobile designs benefit from intuitive controls, ergonomic handling features for relocation, and robust construction to withstand frequent movement and varied factory conditions.
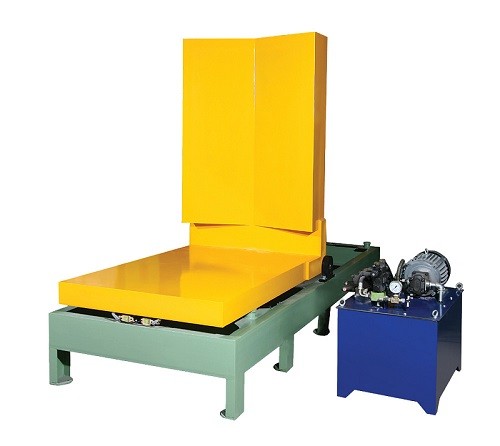

Enhancing Safety and Operability in Mobile Mold Upenders
Mobile mold upenders require specific safety and operational enhancements to address the challenges of movement and varied working environments.
Critical Safety Features
-
Emergency Stop (E-Stop) Buttons: Multiple, easily accessible E-stop buttons are crucial. These should be located on the control panel and potentially at other strategic points on the upender, ensuring operators can quickly halt operation from any position, especially during movement.
-
Proximity Sensors and Collision Avoidance: Integrating proximity sensors can significantly enhance safety by detecting obstacles in the path of the moving upender. These sensors can trigger automatic braking or stop mechanisms to prevent collisions with machinery, structures, or personnel.
-
Audible and Visual Alarms: Alarms that activate during movement and operation are essential for alerting personnel in the vicinity. Flashing lights and distinct audible signals warn others of the upender’s operation, reducing the risk of accidents.
-
Braking and Locking Systems (Redundancy): Beyond standard brakes, redundant braking systems and robust wheel locking mechanisms are vital. These ensure the upender remains securely stationary during operation and prevents unintended rollaway when parked on inclines or uneven surfaces. Fail-safe braking systems, which engage automatically in case of power loss, are also highly recommended.
-
Load Sensors and Overload Protection: Load sensors continuously monitor the weight on the upender platform. Overload protection systems prevent operation if the mold weight exceeds the safe capacity, averting potential structural failures and tip-overs.
Operational Enhancements for Mobility
-
Intuitive and Accessible Controls: Control panels should be designed for ease of use, even during relocation. Wireless remote controls can offer enhanced operator freedom and visibility during movement and positioning. Controls should be clearly labeled and logically arranged for quick and error-free operation.
-
Ergonomic Handles and Steering: For manually moved mobile upenders, ergonomic handles and steering mechanisms are crucial to minimize operator strain and enhance maneuverability. Power-assisted steering can be incorporated for heavier units to reduce physical effort.
-
Robust Construction for Mobile Use: Mobile mold upenders must be built to withstand the stresses of frequent movement and operation in varied factory conditions. Reinforced frames, durable wheel systems, and protective coverings for sensitive components ensure longevity and reliability despite constant relocation.
-
Compact and Balanced Design: A compact footprint and well-balanced design are essential for navigating through factory aisles and tight spaces. Minimizing overall dimensions and optimizing weight distribution makes the upender easier to maneuver and position precisely.
By prioritizing these safety and operational features, mobile mold upenders can offer not only flexibility but also a safe and efficient solution for dynamic mold handling requirements.
4. Applications and Benefits of Mobile Mold Upenders
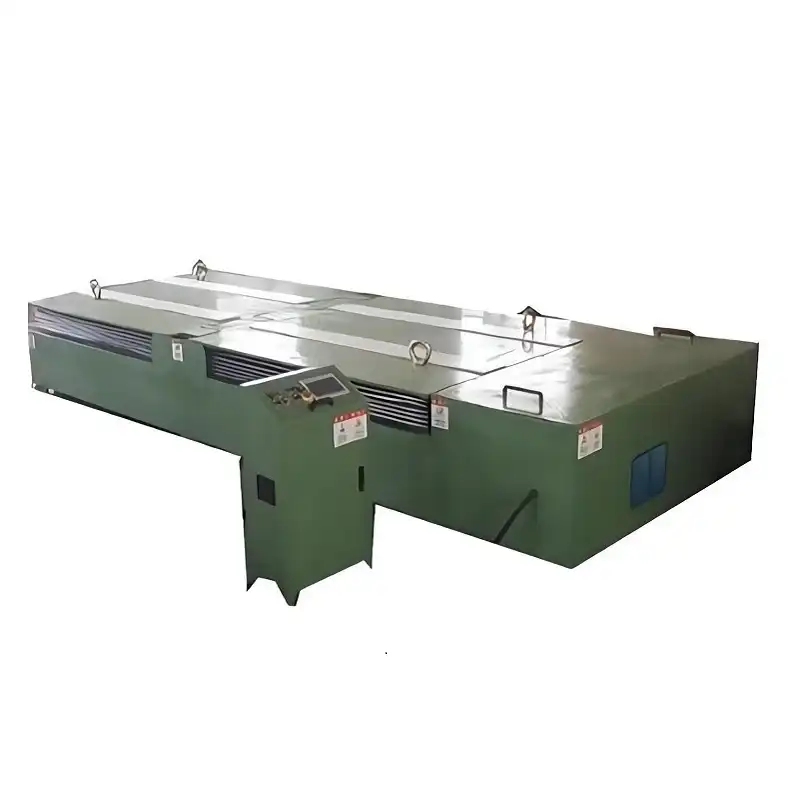

Mobile mold upenders significantly enhance operational flexibility and efficiency in industries dealing with heavy molds. Their ability to be easily relocated and adapted to different production areas provides numerous advantages.
Mobile mold upenders excel in dynamic manufacturing environments where production layouts change frequently, or molds need to be moved between different workstations or storage areas. Industries benefiting most include automotive, aerospace, and large-scale plastic molding, where mold changes and maintenance are common and require flexible, efficient handling solutions. The primary benefit is enhanced workflow and reduced downtime by enabling quicker mold repositioning and maintenance access.
Mobile mold upenders are particularly advantageous in several key scenarios:
-
Flexible Production Layouts: In facilities where production lines are frequently reconfigured to accommodate different product runs or evolving manufacturing processes, mobile mold upenders offer unparalleled adaptability. They can be easily repositioned to align with new layouts, eliminating the need for fixed, location-dependent equipment.
-
Decentralized Workstations: For large manufacturing plants with decentralized workstations dedicated to specific tasks (e.g., mold setup, maintenance, production), mobile upenders facilitate efficient mold transport between these areas. This eliminates bottlenecks and streamlines workflow by bringing the upending capability directly to where it’s needed.
-
Limited Floor Space: In facilities with constrained floor space, mobile mold upenders maximize space utilization. They can be moved out of the way when not in use, freeing up valuable production area. Stationary upenders, in contrast, occupy a fixed footprint, regardless of utilization.
-
Maintenance and Repair Accessibility: Mobile designs allow maintenance crews to bring the upender directly to the mold, rather than transporting heavy molds to a fixed upending station. This significantly simplifies and speeds up mold maintenance and repair procedures, reducing downtime.
-
Cost Efficiency: While the initial investment in mobile mold upenders may be comparable to stationary units, the long-term cost benefits are substantial. Reduced downtime, increased production flexibility, and improved space utilization contribute to a higher return on investment. Furthermore, a single mobile upender can potentially serve multiple production lines or workstations, reducing the need for multiple fixed units.
Conclusion
Implementing a mobile design for mold upenders is a strategic move towards enhancing flexibility, efficiency, and safety in mold handling operations. By carefully considering design elements, power options, safety features, and operational enhancements, manufacturers can leverage mobile mold upenders to optimize workflows, reduce downtime, and adapt to the ever-changing demands of modern manufacturing. Embracing mobile mold upender technology is a key step towards achieving agile and responsive mold handling processes.