Understanding Rotating Rings for Horizontal Orbital Wrappers
In the packaging industry, horizontal orbital wrappers rely heavily on a crucial component: the rotating ring tyre. This essential part provides the structural foundation that enables the film carriage to revolve around a product, ensuring a consistent and secure wrap. Understanding the function and types of rotating rings is vital for optimizing packaging operations. This article explores the role of the rotating ring, details the common types available, and discusses their manufacturing processes, characteristics, and suitability for different applications.
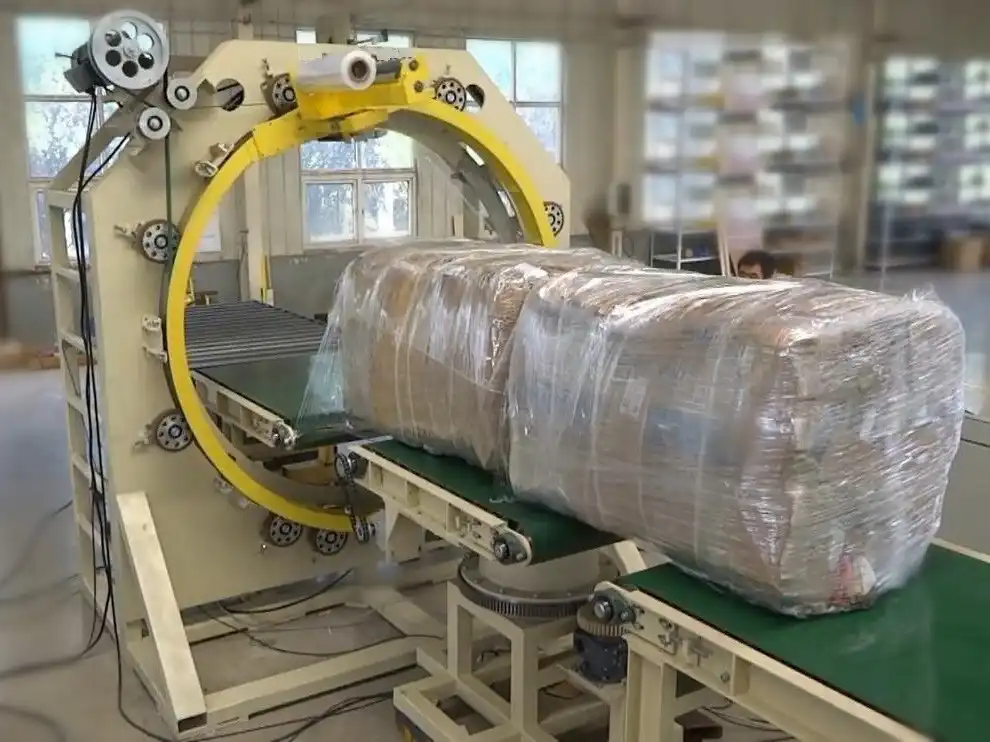

The Core Function of the Rotating Ring in Orbital Wrapping
The rotating ring serves two primary functions in a horizontal orbital wrapper, directly impacting wrap quality and efficiency:
- Enabling 360-Degree Rotation: The ring provides a smooth, continuous track for the film carriage assembly. This allows the wrapping film (like stretch film) to be applied evenly around the entire circumference of the package, crucial for products like pipes, lumber, doors, or bundles. Consistent application minimizes film waste and ensures uniform protection.
- Supporting and Guiding the Film Carriage: The ring securely holds and guides the film carriage, which houses the film roll and pre-stretch mechanism. This stable fixation maintains the necessary film tension throughout the wrapping cycle, leading to a tight, secure, and load-stable wrap. Proper guidance prevents derailment and ensures operational reliability.
Key Types of Rotating Ring Tyres
The design and material of the rotating ring influence the wrapper's speed, load capacity, maintenance needs, and overall cost. The choice depends heavily on the specific packaging requirements. Here are the main types used in horizontal orbital wrappers:
1. Aluminum Cast Rings
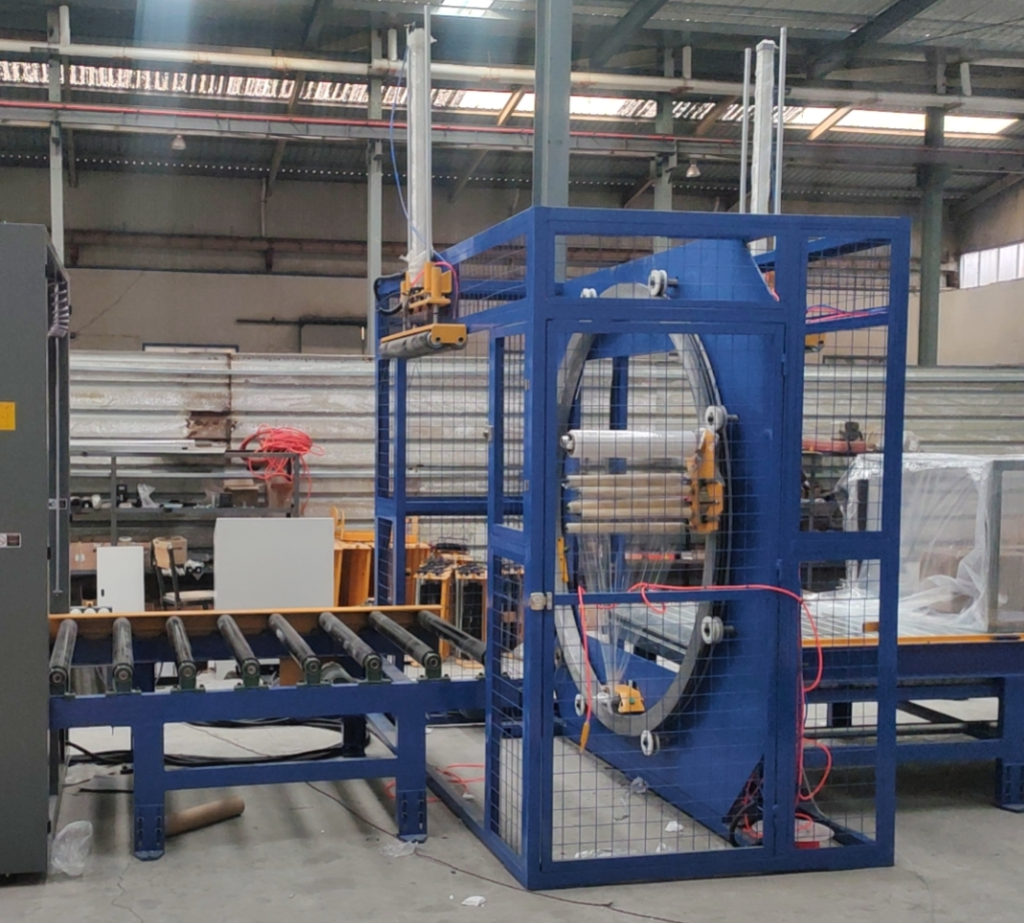

- Production Process:
- Molten aluminum is poured into a custom mold (casting).
- The cooled casting undergoes precision machining to achieve exact dimensions and smoothness.
- Mounting holes are drilled according to specifications.
- Key Specifications:
- Outer Diameter (OD): Typically ranges from 200 mm to 2200 mm.
- Custom Sizes: Larger diameters, up to 4000 mm or more, can be manufactured for specialized applications.
- Thickness: Varies depending on the ring's diameter and the anticipated load from the film carriage and wrapping tension.
- Advantages:
- Lightweight: Aluminum's lower density reduces rotational inertia, allowing for higher wrapping speeds and potentially less powerful drive motors. Easier handling during maintenance.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Offers good structural integrity despite being light.
- Good Machinability: Allows for precise finishing.
- Disadvantages:
- Mold Costs: Requires the creation of specific casting molds for each size, which can be expensive, especially for low-volume or custom rings. This adds to initial cost and lead time.
- Material Cost: Aluminum is generally more expensive than steel.
- Ideal Applications: High-speed wrapping lines where minimizing rotational mass is beneficial; standard machine sizes where mold costs can be amortized over volume.
2. Fabricated Steel Rings
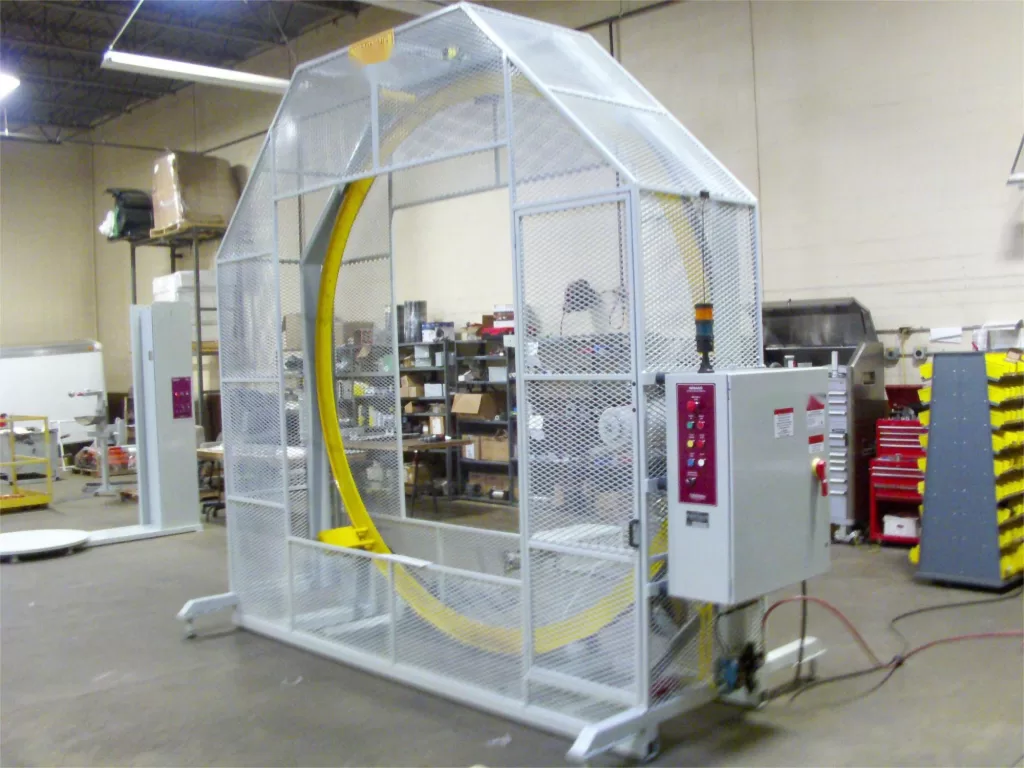

- Production Process:
- Steel plates or bars are bent or rolled into a circular shape.
- The ends are welded together to form a continuous ring.
- The welded ring is machined for precise dimensions, flatness, and surface finish.
- Mounting holes are drilled.
- Key Specifications:
- Outer Diameter (OD): Commonly available from 200 mm up to 2500 mm, with larger custom sizes feasible.
- Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than cast aluminum rings, especially for larger or custom sizes, as no specialized molds are needed.
- High Structural Strength: Steel provides excellent rigidity and load-bearing capacity.
- Flexibility: Easier to produce custom diameters without high initial tooling costs.
- Disadvantages:
- Heavy: Steel's high density results in a heavier ring, increasing rotational inertia and potentially limiting maximum wrapping speed or requiring more powerful drive systems. More difficult to handle during maintenance.
- Potential for Wear: The contact surfaces, especially where drive wheels engage, can be prone to wear over time, potentially requiring resurfacing or replacement.
- Lower Maximum Speed: Due to the higher weight and potential balance issues compared to precision-cast rings.
- Ideal Applications: Cost-sensitive applications; heavy-duty wrapping where high speeds are not the primary concern; large or custom diameter requirements.
3. Bearing-Based Rings (Slewing Rings)
- Production/Source:
- These are typically standard industrial components known as slewing rings or turntable bearings.
- They are sourced directly from specialized bearing manufacturers. No custom fabrication of the ring itself is usually needed, only integration into the wrapper design.
- Key Specifications:
- Outer Diameter (OD): Wide range available, from around 200 mm to over 6000 mm.
- Integrated System: Combines the rotating element and bearing function into a single unit, often with integrated gear teeth for driving.
- Advantages:
- High Speed and Precision: Engineered for smooth, low-friction rotation, enabling very high wrapping speeds and precise movement.
- High Load Capacity: Designed to handle significant axial, radial, and tilting moment loads simultaneously.
- Integrated Drive Option: Often available with internal or external gear teeth for direct pinion drive.
- Disadvantages:
- High Cost: Significantly more expensive than cast aluminum or fabricated steel rings, especially at larger diameters.
- Weight: Can be quite heavy, particularly larger sizes, impacting overall machine design.
- Complexity: Integration and maintenance might require specialized knowledge compared to simpler ring types.
- Ideal Applications: High-performance orbital wrappers demanding maximum speed, precision, and high load capacity; applications requiring very smooth rotation.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Rotating Ring
Choosing the appropriate rotating ring type involves balancing several factors:
- Package Dimensions and Weight: Larger, heavier packages may necessitate the strength of steel or a robust bearing ring.
- Required Wrapping Speed (Throughput): For high throughput lines, the lower inertia of aluminum or the engineered performance of a bearing ring is often preferred.
- Budget Constraints: Fabricated steel rings offer the most economical solution, while bearing rings represent the highest investment.
- Operating Environment: Consider factors like temperature, humidity, and potential contaminants that might affect material choice or maintenance requirements (e.g., corrosion resistance).
- Maintenance Resources: Bearing rings might require specialized lubrication and monitoring, while steel rings may need attention to wear on contact surfaces.
Maintenance and Longevity
Regardless of type, proper maintenance is key to the longevity and performance of the rotating ring and the orbital wrapper:
- Lubrication: Bearing rings require periodic lubrication according to manufacturer specifications. The contact points between drive wheels and aluminum/steel rings may also benefit from appropriate lubrication or dry-running compatible materials.
- Cleaning: Keeping the ring and track surfaces clean prevents abrasive wear and ensures smooth operation.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect rings (especially steel) and drive components for signs of wear, damage, or misalignment. Check fasteners for proper torque.
- Component Replacement: Drive wheels, support rollers, and bearings eventually wear out and require replacement as part of preventative maintenance.
Conclusion
The rotating ring tyre is more than just a circular track; it's a fundamental component determining the capability and efficiency of a horizontal orbital wrapper. Whether choosing a lightweight aluminum cast ring for speed, a cost-effective fabricated steel ring for robustness, or a high-precision bearing ring for demanding performance, the selection directly impacts the packaging process. By carefully considering the application requirements—speed, load, budget, and maintenance—manufacturers can select the optimal orbital wrapper ring type. This ensures reliable operation, consistent wrap quality, and efficient packaging, ultimately contributing to a smoother and more productive end-of-line process.