Optimizing Product Protection: A Guide to Packaging Requirements for Horizontal Orbital Wrappers
Selecting the appropriate packaging solution is fundamental to protecting products during handling and transportation. Effective packaging prevents damage, minimizes costs associated with returns or replacements, and preserves product integrity until it reaches the end-user. As industries increasingly adopt automation, understanding the capabilities and requirements of machinery like the horizontal orbital wrapper becomes crucial for optimizing operations.
This guide explores the key factors in determining the right type of packaging for various products when using an orbital wrapping system. We will delve into assessing product characteristics, evaluating current processes, and understanding the technical specifications needed to ensure your chosen stretch packaging strategy is both efficient and effective.
1. The Importance of Packaging in Modern Logistics
Packaging serves a role far beyond simple containment; it is a critical component of the supply chain. In today's fast-paced global market, the quality of your packaging directly impacts product integrity, cost efficiency, and customer perception.
1.1 Reducing Damage During Transit
A primary function of packaging is to minimize the risk of damage during shipping and handling. Products inadequately packaged are susceptible to shifting, impacts, abrasion, and environmental factors. A well-designed packaging strategy, often incorporating stretch wrapping, secures items, reducing the likelihood of damage throughout the logistics journey. Consider factors like vibration, compression, and potential drops when evaluating protection needs.
1.2 Improving Operational Efficiency
Integrating automated systems like horizontal orbital wrappers can dramatically enhance operational efficiency. Automation provides consistent application, predictable cycle times, and reduced reliance on manual labor compared to manual packaging. This allows businesses to increase throughput, ensure reliable packaging quality, and potentially lower labor costs associated with packaging tasks.
1.3 Enhancing Brand Image and Customer Satisfaction
The condition in which products arrive significantly influences customer perception. Professional, secure packaging that effectively protects the contents reflects positively on your brand. Conversely, goods arriving damaged due to poor packaging can negatively impact customer relationships and brand reputation. Consistent, high-quality packaging is an extension of your brand's commitment to quality.
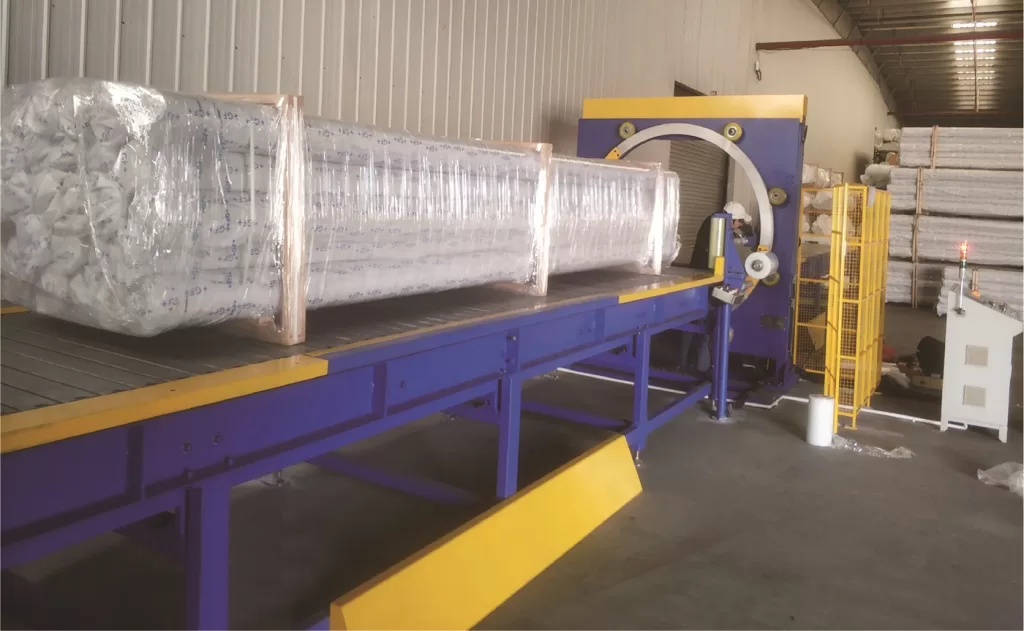

2. Identifying Products Requiring Wrapping
The first step towards an effective packaging strategy is a thorough assessment of the products needing protection. Key characteristics will dictate the most suitable type of packaging and wrapping parameters.
2.1 Product Dimensions and Shape
The size and geometry of a product heavily influence packaging requirements.
- Long, narrow items: Pipes, lumber, extrusions, and beams often benefit from orbital wrapping to provide consistent containment along their length.
- Irregularly shaped items: May require specific wrapping patterns or additional void fill/dunnage to ensure complete protection and stability.
- Bundled items: Securing multiple items together requires sufficient film tension and overlap.
2.2 Fragility and Handling Needs
Assess the inherent fragility of your products.
- Delicate items: Require careful consideration of film type, tension settings, and potentially additional protective materials (e.g., edge protectors, foam) to cushion against impacts and vibration. Stretch film layers can provide shock absorption.
- Robust items: May require less complex wrapping but still need securing to prevent surface damage or movement.
2.3 Bulk Packaging vs. Individual Packaging
Determine the unit of handling for packaging.
- Bulk packaging: Wrapping multiple units together can be efficient but requires ensuring the bundle is stable and individual items won't damage each other. Load containment is key.
- Individual packaging: Provides tailored protection for each item but can increase material usage and cycle time per item.
3. Evaluating Your Current Packaging Process
Before implementing changes or investing in new equipment like a horizontal orbital wrapper, analyze your existing packaging methods to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement.
3.1 Manual vs. Automated Packaging Assessment
Compare your current approach:
- Manual Packaging: Often characterized by variability in wrap quality, higher labor intensity, potential ergonomic risks, and inconsistent material usage (wasted materials).
- Semi-Automated/Automated Packaging: Offers improved consistency, higher throughput potential, optimized material usage, and reduced manual labor. An orbital wrapper represents a step towards automation.
3.2 Packaging Efficiency, Throughput, and Bottlenecks
Quantify your current performance:
- Current Output: How many items/packages are processed per hour/day?
- Cycle Time: How long does it take to package one unit?
- Bottlenecks: Where do delays occur in the current process? Understanding these metrics helps justify investment in automation and sets benchmarks for improvement.

4. Determining Your Required Daily Packaging Output
Your target daily packaging output is a critical factor in selecting appropriately sized and specified machinery.
4.1 Scaling Packaging Operations for Growth
Consider future needs. If your business anticipates growth, select a packaging solution with the capacity to handle increased volume. An orbital wrapping machine with adjustable speed settings or programmability offers flexibility to adapt to changing demand without becoming a limiting factor.
4.2 Minimizing Downtime and Ensuring Consistency
Manual processes are often susceptible to downtime caused by labor availability, fatigue, or inconsistencies. Automation significantly reduces these variables, enabling a more predictable and reliable daily packaging output. Well-maintained automated systems provide dependable performance shift after shift.
5. Assessing and Mitigating Transit Damage
Reducing damage during transit is a primary driver for optimizing packaging. Analyze past instances of damage to understand root causes.
5.1 Common Causes of Transit Damage
Damage often results from:
- Insufficient Containment: Using inadequate stretch film layers, incorrect tension, or poor wrapping patterns allows products to shift or separate.
- Improper Handling: Drops, impacts, and vibration during loading, unloading, and transport.
- Environmental Factors: Moisture, temperature fluctuations, and contaminants.
- Stacking Issues: Compression damage from improperly stacked loads.
5.2 Selecting Appropriate Packaging Materials
The choice of materials is vital:
- Stretch Film: Select the correct type (cast vs. blown), gauge (thickness), and pre-stretch level for the load characteristics. Using film that is too thin compromises protection, while overly thick film increases cost unnecessarily.
- Protective Additives: Consider edge protectors, corner boards, foam, or bubble wrap for fragile areas or sharp edges. The orbital wrapper must accommodate these additions if used.

6. Custom Packaging Solutions for High-Value or Delicate Goods
Products that are high-value, fragile, or have specific handling requirements often necessitate custom packaging solutions beyond standard wrapping protocols.
6.1 Tailored Wrapping Programs
Modern orbital wrappers often allow for customizable wrapping programs:
- Multi-layer wrapping: Applying additional layers of stretch film to specific areas for enhanced protection.
- Variable Tension: Adjusting film tension during the wrap cycle for optimal containment without crushing sensitive parts.
- Specialized Patterns: Creating reinforced bands or specific overlaps to address weak points.
6.2 Considerations for Fragile, Perishable, or Sensitive Items
- Fragile Items: Require maximum cushioning and securement to prevent breakage from impact or vibration.
- Perishable Goods: May need breathable films or integration with temperature-controlled packaging systems.
- Surface-Sensitive Items: Require non-abrasive films or protective layers to prevent scratches or marks.
7. Defining Maximum and Minimum Packaging Dimensions
Accurately determine the size range (length, width, height) of the products your orbital wrapping machine must accommodate. This is crucial for selecting a machine with the appropriate ring size and capacity.
7.1 Machine Specifications and Adjustability
- Ring Size: The wrapper's ring diameter dictates the maximum cross-section of the product that can pass through.
- Adjustable Guides: Ensure the machine has guides or supports that can be adjusted for the minimum and maximum product dimensions.
- Flexibility: If you package a wide variety of sizes, choose a machine designed for flexibility to minimize changeover time.
7.2 Optimizing Packaging for Space Efficiency
While ensuring protection, aim to minimize package dimensions to optimize warehouse space and transportation costs. Efficient wrapping avoids excessive material usage and keeps the overall package footprint as small as possible.
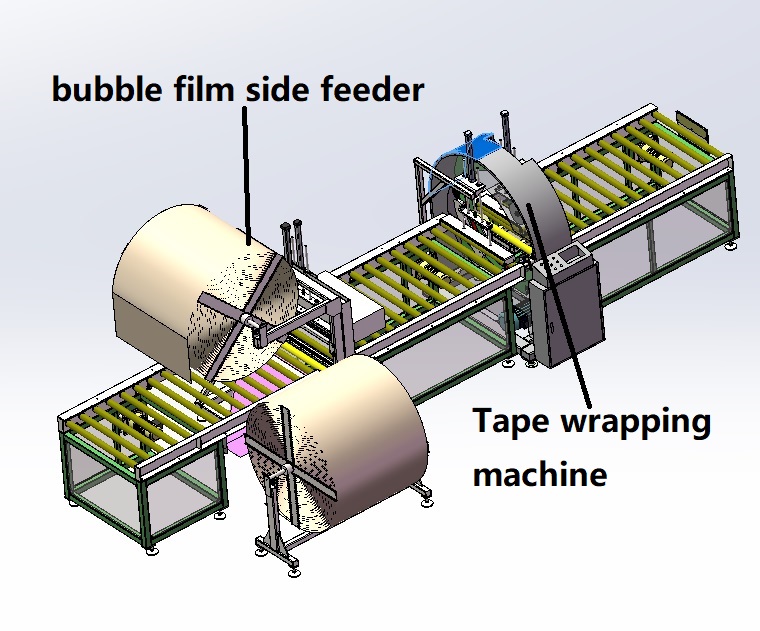
8. Stacking Height Considerations for Wrapped Goods
The intended stacking height of packaged goods impacts stability requirements and, consequently, the wrapping strategy.
8.1 Ensuring Stack Stability
Properly wrapped loads must maintain integrity when stacked. Key factors include:
- Load Containment: Sufficient stretch film tension and overlap are needed to unitize the load and prevent layers from shifting.
- Even Weight Distribution: Ensure the load itself is stable before wrapping.
- Interlocking Patterns: Wrapping can help lock layers together for improved stability.
8.2 Maximizing Vertical Storage Space
Effective wrapping enables safe stacking, allowing businesses to utilize vertical warehouse space efficiently. The wrapping machine must apply film consistently to ensure loads are stable enough for the planned stacking height.
9. Establishing Maximum and Minimum Package Weights
The weight range of your packages directly influences machine selection and wrapping parameters.
9.1 Handling Heavy Loads Securely
- Robust Machine Construction: Ensure the wrapper's frame, conveyor, and drive systems can handle the maximum weight without strain.
- Sufficient Film Tension: Heavier loads require higher film tension and potentially stronger film (higher gauge) to ensure secure containment. Adjustable tension control is essential.
- Conveyor Capacity: Verify that the integrated or standalone conveyor system is rated for the maximum load weight.
9.2 Protecting Lightweight Goods Effectively
- Controlled Tension: Lightweight or crushable items require lower, precisely controlled film tension to avoid damage. The machine must offer fine control at lower tension settings.
- Gentle Handling: Ensure conveyor speeds and transitions are smooth to prevent jostling delicate items.
10. Evaluating Needs for Integrated Weighing and Labeling
Consider if additional functions integrated into the packaging line could streamline your process.
10.1 Integrated Weighing Systems
- Functionality: Some orbital wrapping machines can incorporate scale systems to weigh packages post-wrapping.
- Benefits: Provides accurate weights for shipping manifests and cost calculation, aids in quality control (verifying contents), and integrates data capture into the workflow.
10.2 Automatic Labeling Applicators
- Functionality: Systems that automatically print and apply shipping labels, barcodes, or product identification tags as part of the wrapping cycle.
- Benefits: Reduces manual handling, improves labeling accuracy and consistency, and increases overall throughput by eliminating a separate labeling step.
11. Product Placement and Orientation on the Conveyor
How products are fed into the orbital wrapping machine impacts wrap quality and efficiency, especially in automated packaging lines.
11.1 Ensuring Correct Alignment for Optimal Wrapping
- Centering: Products should ideally be centered as they enter the wrapping ring for even film application.
- Orientation: Consistent orientation is crucial for repeatable wrapping patterns.
- Guides and Sensors: Use adjustable side guides and sensors to ensure proper product positioning before wrapping commences. Misaligned items can lead to poor wraps and potential jams.
11.2 Conveyor System Compatibility and Integration
- Seamless Flow: Ensure the wrapper's conveyor integrates smoothly with upstream and downstream equipment.
- Speed Synchronization: Conveyor speeds should be synchronized for efficient transfer.
- Type Compatibility: Verify compatibility with belt, roller, or chain conveyors depending on your product and system.
12. Determining if Layering or Specialized Wrapping is Needed
Certain products benefit from layering or specific wrapping techniques for enhanced protection.
12.1 Multi-Layer Packaging for Enhanced Protection
- Application: Applying multiple layers of stretch film, either overall or in specific bands, adds cushioning and strength, particularly for fragile goods or items with sharp corners.
- Machine Capability: Ensure the orbital wrapper's control system allows for programming multi-layer wraps or specific banding patterns easily.
12.2 Balancing Protection and Material Efficiency
While layering adds protection, optimize the number of layers to avoid unnecessary material waste and cost. Modern wrappers often feature controls to precisely manage film usage based on programmable recipes for different products, finding the right balance between security and economy.
13. Requirement for Timber Supports or Pallets
Assess whether your products need to be placed on pallets, skids, or incorporate timber supports before or during wrapping.
13.1 The Role of Pallets and Supports in Secure Packaging
- Handling: Pallets facilitate easy movement using forklifts or pallet jacks.
- Stability: Provide a stable base for large, heavy, or awkwardly shaped items.
- Protection: Elevate products off the floor and provide a structural base.
- Unitization: Essential for securing multiple items together as a single unit load.
13.2 Wrapping Solutions for Palletized or Supported Goods
- Machine Clearance: Ensure the orbital wrapper has adequate clearance to accommodate the product plus the pallet or timber supports.
- Wrap-to-Pallet: Some techniques involve securing the load to the pallet with the stretch film for maximum stability. Verify the machine can perform such patterns if needed.

14. Calculating Your Average Packaging Rate (Throughput)
Know your required average packaging rate (e.g., packages per hour or per day) to select a machine with adequate speed and capacity.
14.1 Matching Machine Speed to Operational Demand
- Machine Cycle Time: Understand the wrapper's theoretical maximum speed (e.g., RPM of the ring) and realistic throughput considering product loading/unloading.
- Meeting Targets: Choose a machine capable of exceeding your current or projected peak demand to avoid the packaging station becoming a bottleneck. Adjustable speed controls offer operational flexibility.
14.2 Avoiding Production Bottlenecks
An undersized or slow wrapping machine can hinder overall production flow, leading to delays and reduced efficiency. Analyze your entire production line to ensure the packaging step aligns with the output of preceding and succeeding processes.
15. Considering Operational Shifts and Machine Durability
The number of daily operating shifts influences the requirement for machine robustness and reliability.
15.1 Durability and Reliability for Continuous Operation
- Heavy-Duty Construction: Machines intended for multi-shift or 24/7 operation typically feature more durable components, robust frames, and higher-quality motors and electronics.
- Maintenance Requirements: Consider the recommended maintenance schedule. Reliable machines designed for continuous use often have features simplifying maintenance to minimize downtime. [Link to reputable maintenance best practices guide].
15.2 Minimizing Downtime Between Shifts and During Operation
- Automation Benefits: Automated systems require less operator intervention, facilitating smoother transitions between shifts.
- Reliability: Choosing a high-quality, well-maintained machine minimizes unexpected breakdowns that can halt production across shifts. Look for features like quick film roll changes and fault diagnostics.

Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Packaging Solution
Choosing the right horizontal orbital wrapper and associated packaging strategy is a multi-faceted process crucial for operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and customer satisfaction. By systematically evaluating:
- Product characteristics (size, shape, weight, fragility)
- Current process inefficiencies
- Required throughput and operational demands (shifts, output rates)
- Specific protection needs (layering, supports, damage mitigation)
- Integration requirements (conveyors, weighing, labeling)
You can identify a packaging solution that not only protects your goods effectively during transit but also optimizes your workflow and supports your business goals. Investing thoughtfully in appropriate packaging automation and materials ensures products arrive safely, reinforcing brand quality and minimizing losses associated with damage.